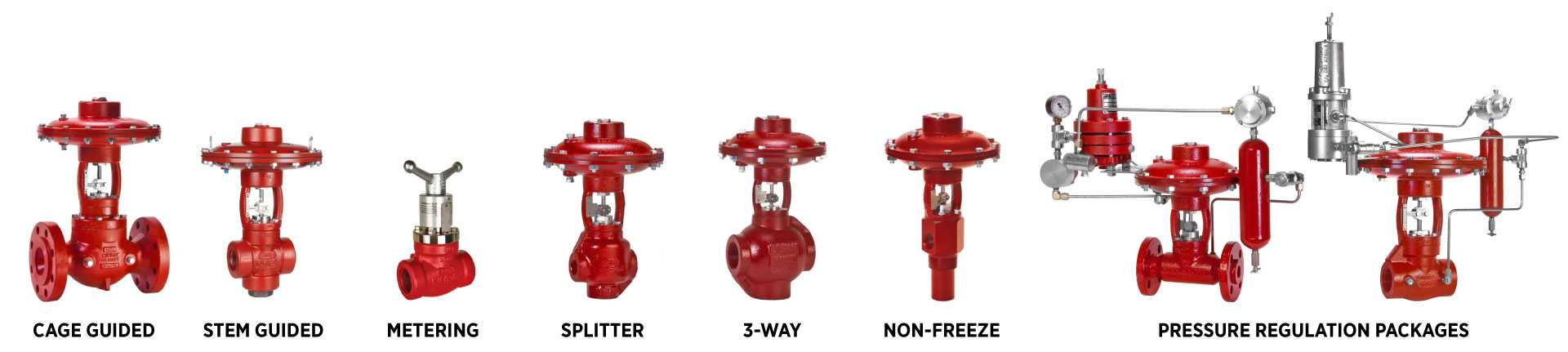

High Pressure Control Valves are some of the most versatile and durable components used in oil and gas operations. Depending on what they’re paired with—a pressure pilot, level controller, thermostat, or level switch—they can control pressure, level, flow, or temperature across your system.
A control valve by itself doesn’t do anything; it simply stays either open or closed (its fail position) until it receives a signal telling it to move. Once paired with the right control device, though, it can do so much on your site.
Common HPCV Applications
High Pressure Control Valves can be used in a wide variety of applications, including:
Liquid Dump
When paired with a level controller or level switch, a high pressure control valve can control liquid levels inside vessels or separators.
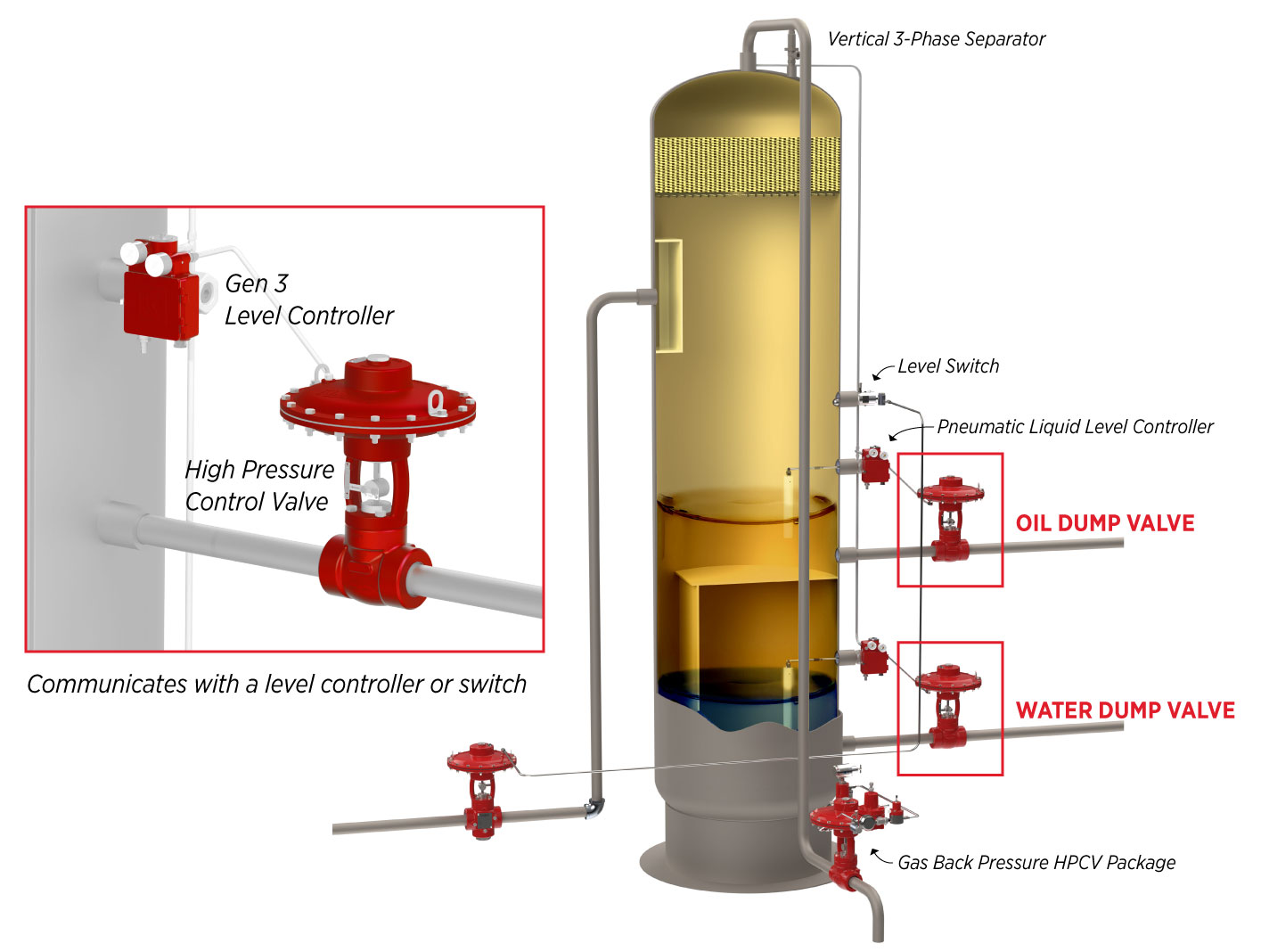
Pressure Regulation
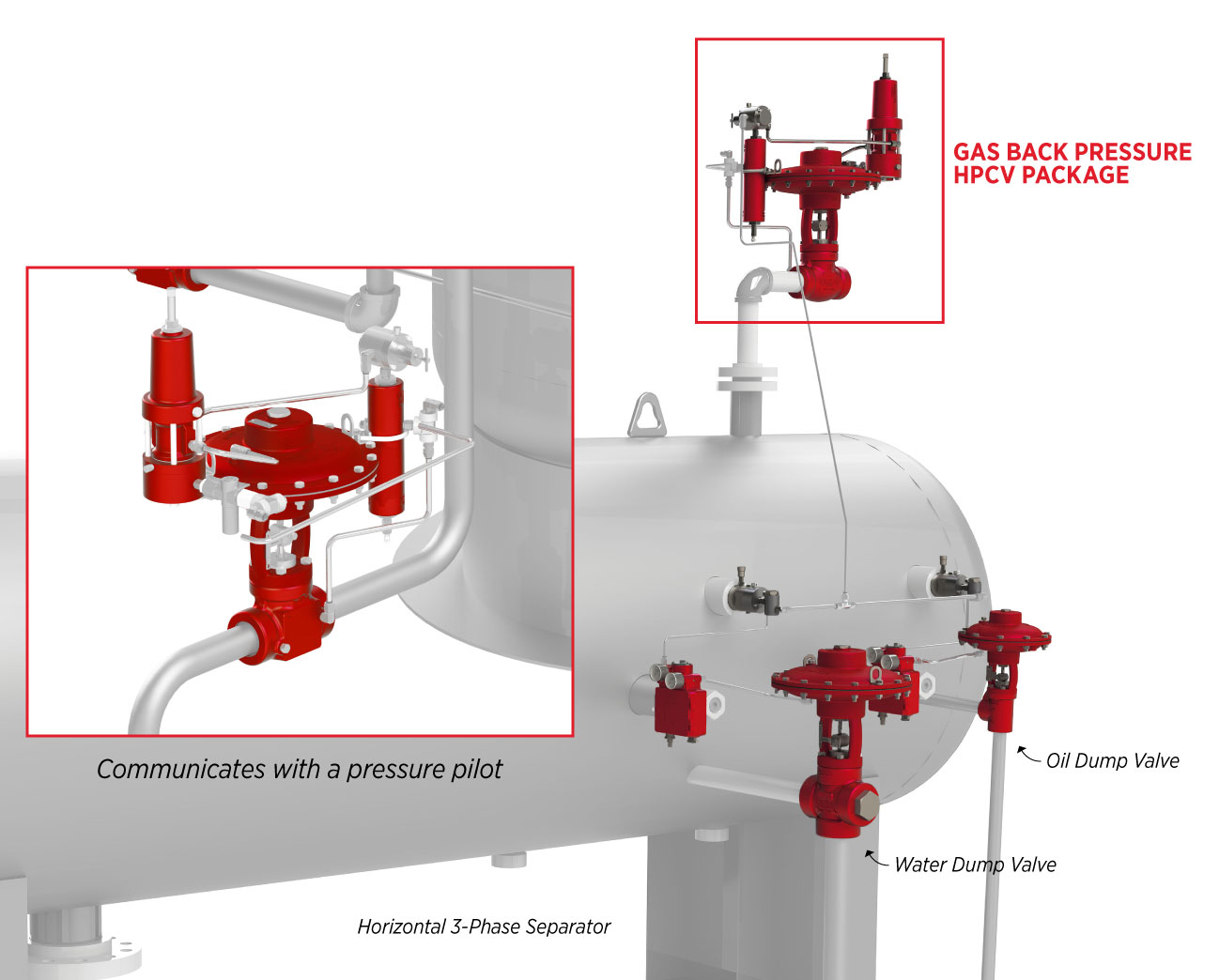
When combined with a pressure pilot and other components, a HPCV becomes part of a pressure control package.
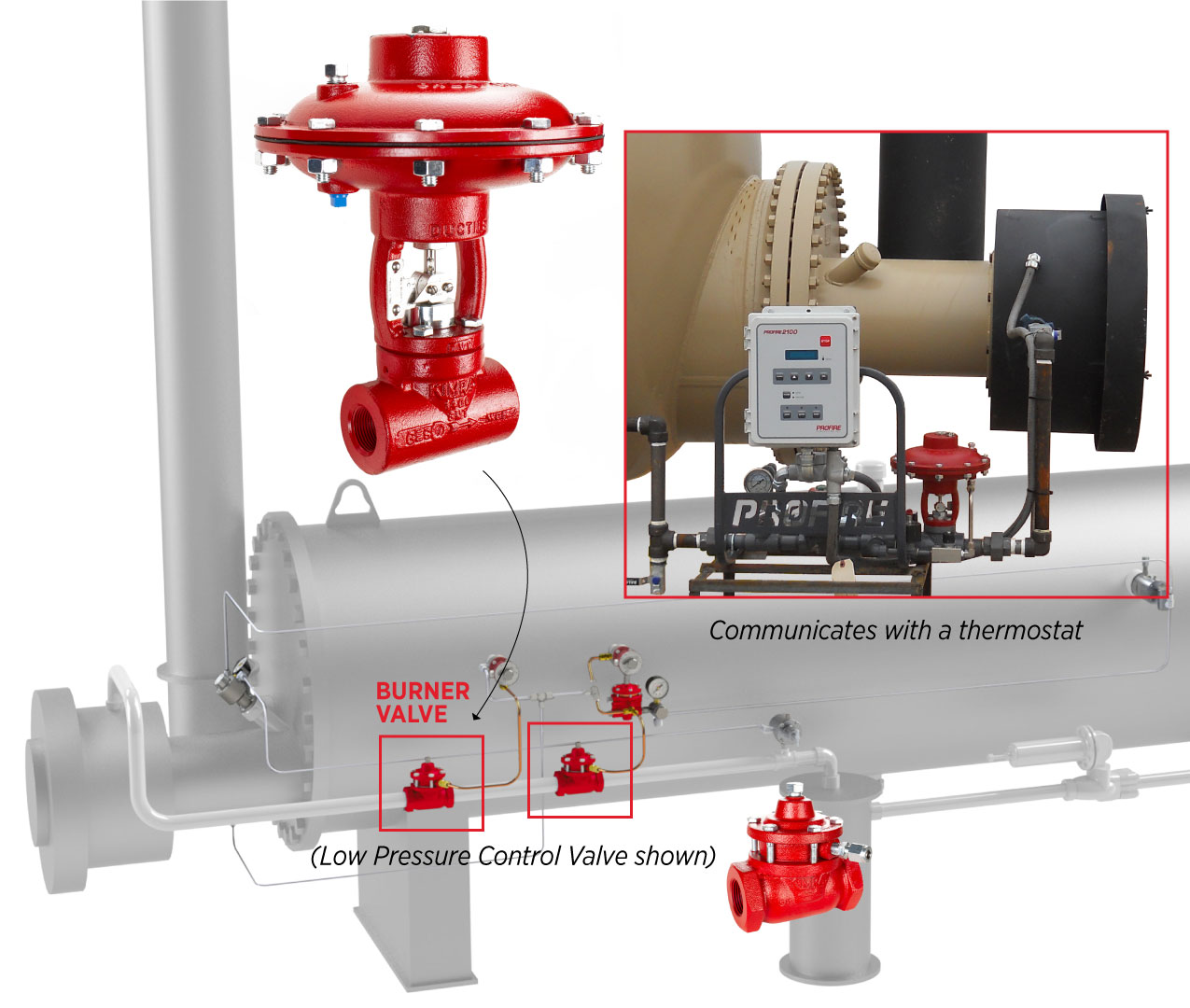
Temperature Control
The 1" HPCV is often used for controlling burner fuel gas in heater applications because of their precise control when used with small trim sets.
Flow Control or Metering
Metering valves are a category of Kimray high pressure control valves that can be set to a specific position to throttle or choke pressure.
Splitter & 3-Way
Divert flow between two process lines.
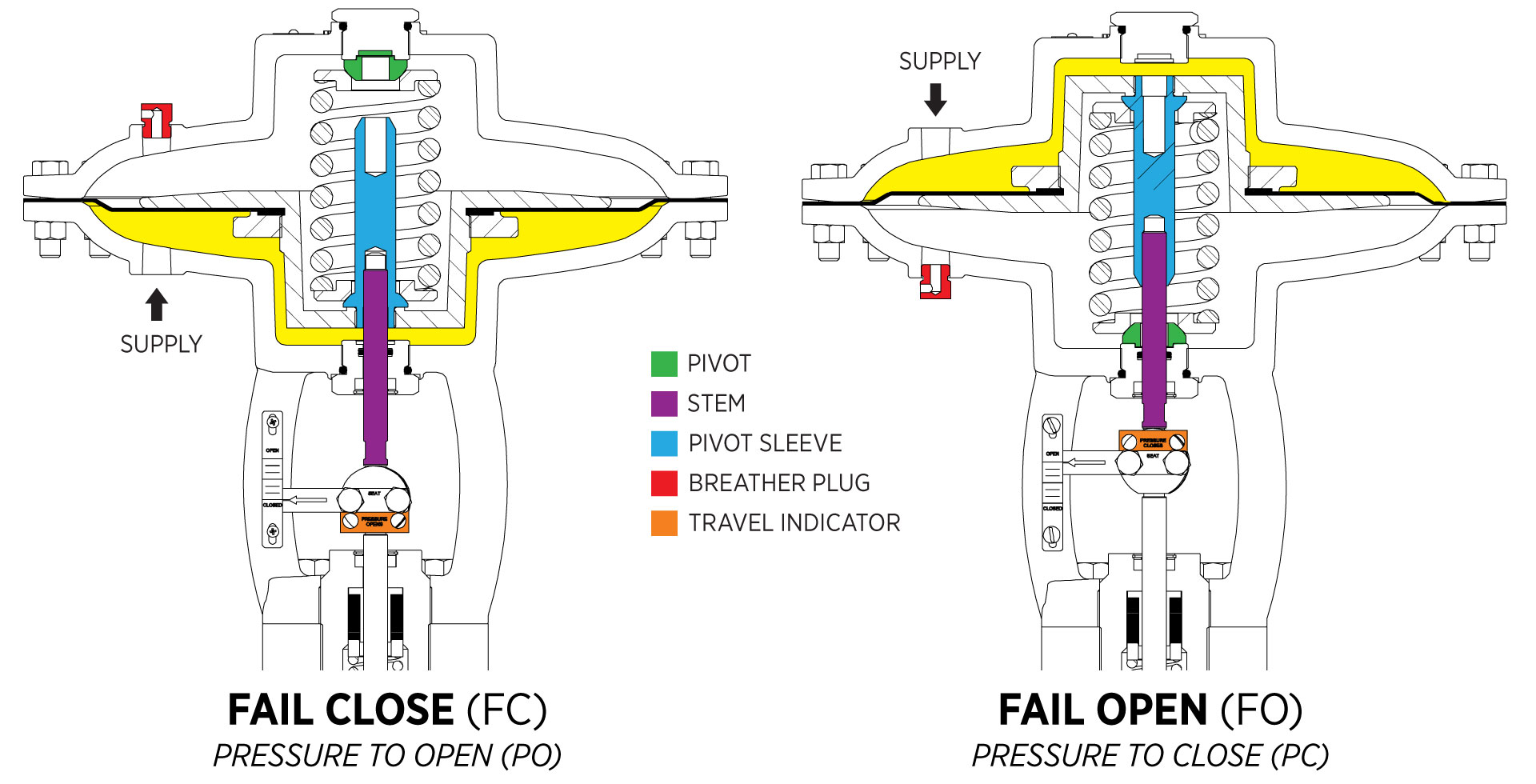
Fail Positions: Pressure-to-Open vs. Pressure-to-Close
Every HPCV has a default fail position which is what the valve does when it loses its signal.
- Fail-Close (FC) a.k.a. Pressure-to-Open (PO): It takes pressure to open the valve.
- Fail-Open (FO) a.k.a. Pressure-to-Close (PC): It takes pressure to close the valve.
General Application Fail Positions
- Back pressure: Fail-open to protect upstream equipment.
- Pressure reducing: Fail-close to protect downstream equipment.
HPCV actuators are field-reversible meaning their fail position can be converted. Switching between the two is easy and requires no extra components.
How to Reverse Topworks from Fail Close to Fail Open
Stem Guided vs. Cage Guided
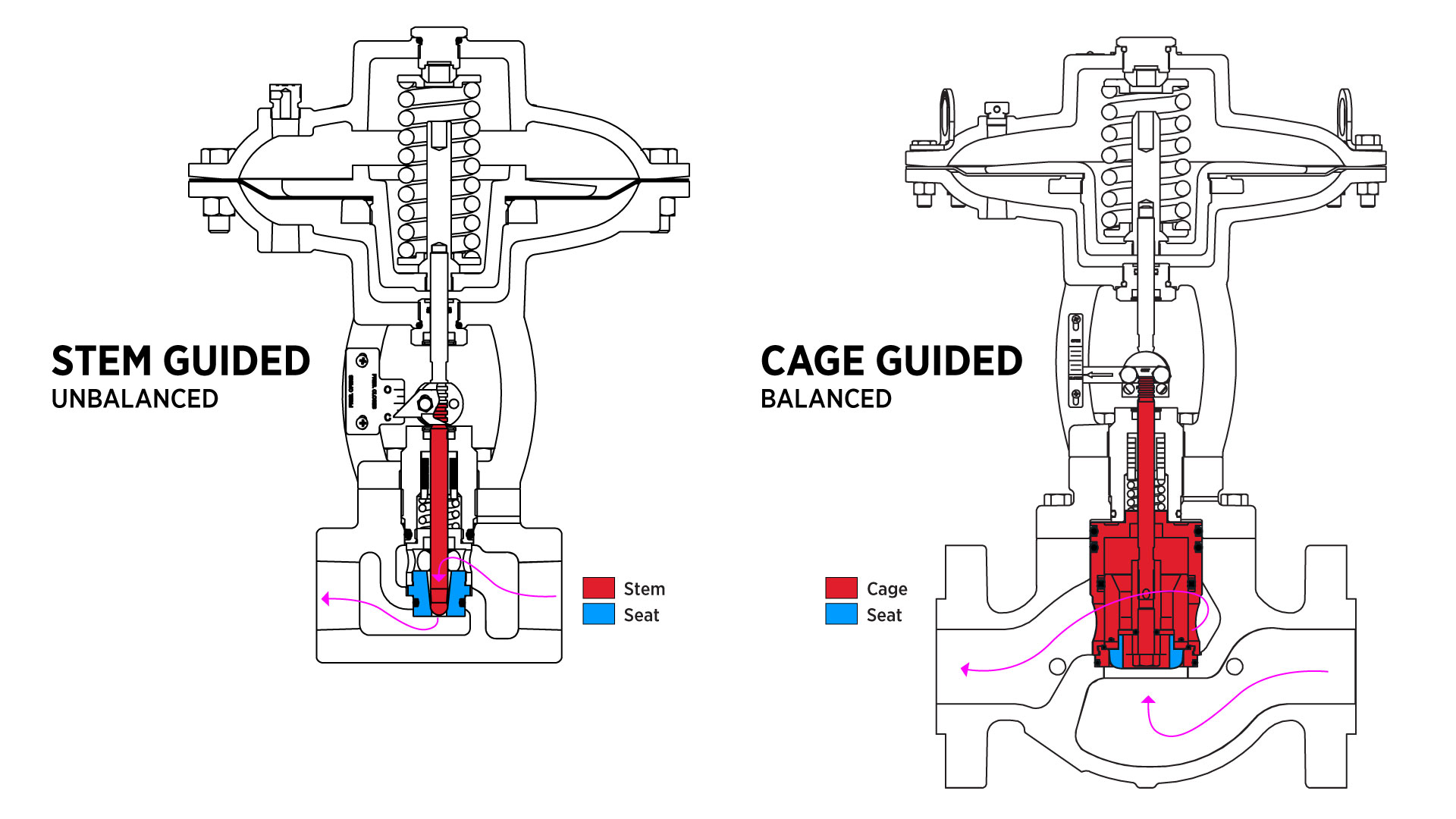
Cage Guided (Balanced) Valves
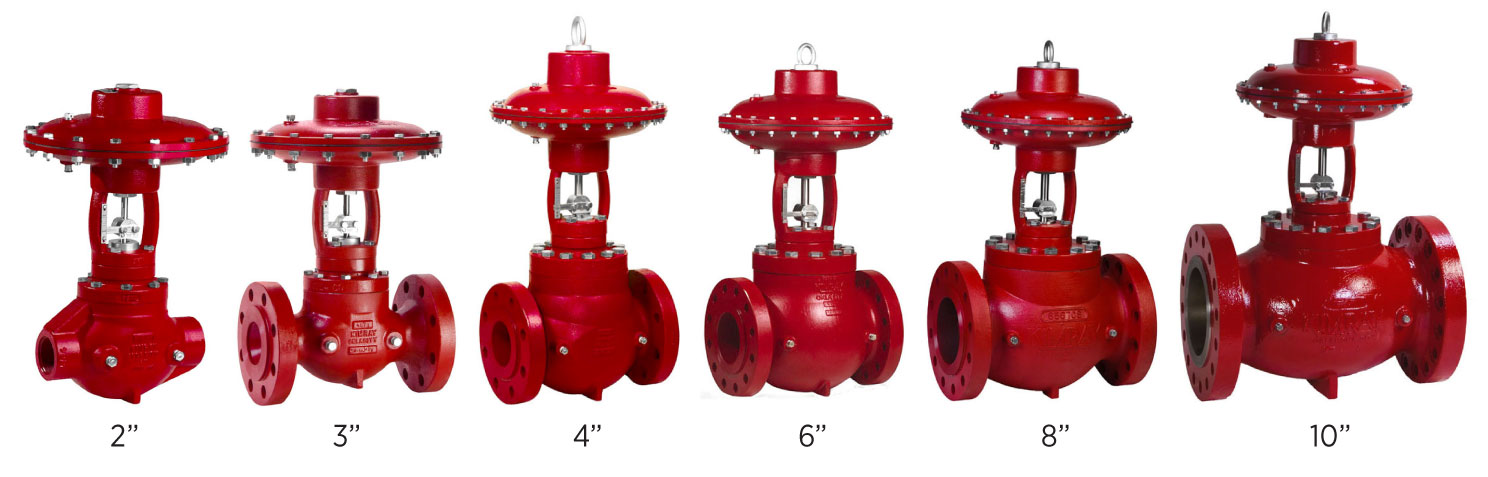

Cage-guided valves are balanced control valves, meaning upstream pressure is equalized above and below the piston assembly. This allows the valve to open easily even against large pressure differentials.
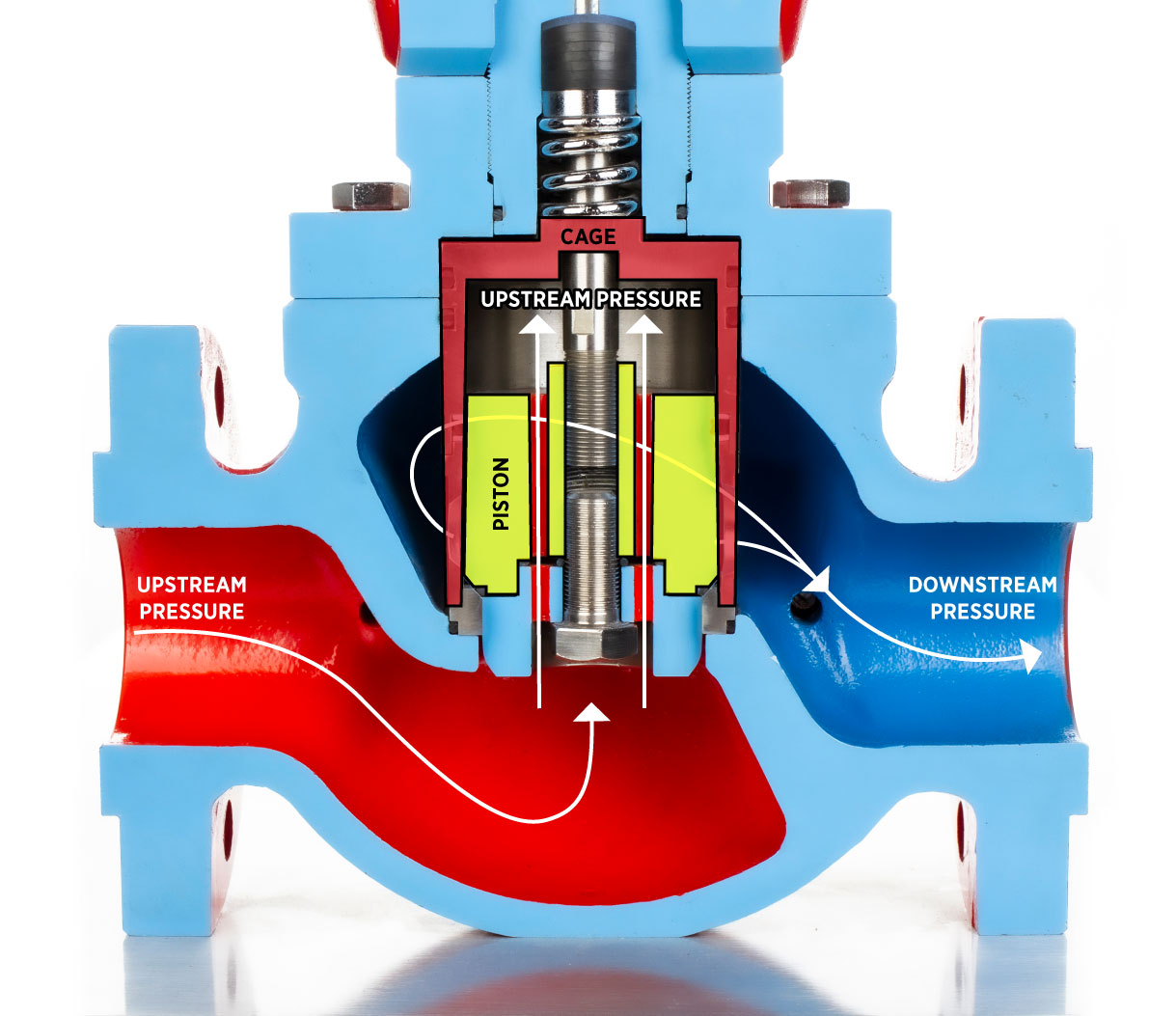
- Connection Sizes: 2″ to 10″ (RF/Flanged; NPT on 2" only)
- Body Styles: Through body
- Flow Range: Cv 28.6 to 1091 (Valve Flow Coefficient)
- Seal Class: Class VI (bubble-tight seal with a rubber seat and metal-to-metal backup)
- Ideal For: High flow or high differential pressure applications
Stem Guided (Unbalanced) Valves
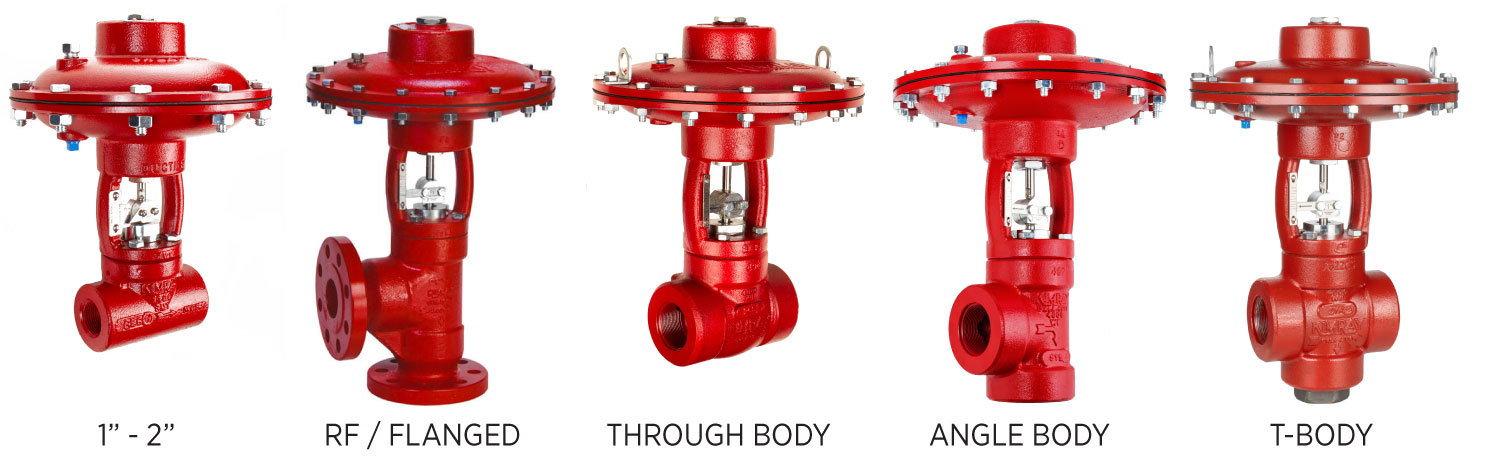

Stem-guided valves are unbalanced, meaning upstream pressure pushes on top of the ball while downstream pressure pushes below. This design makes them great when control precision is key.
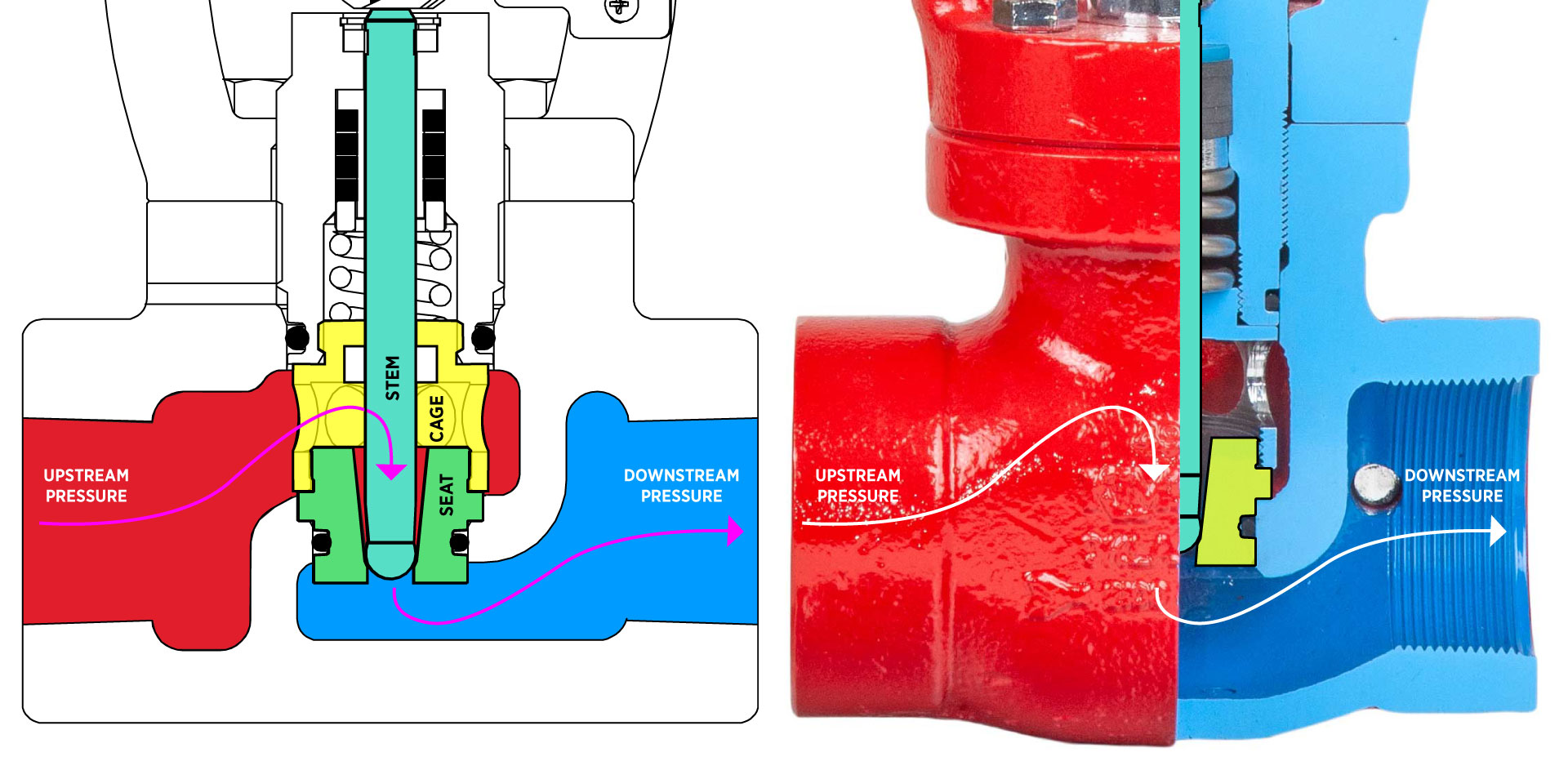
- Connection Sizes: 1″ and 2″ (flanged, threaded,
- Body Styles: Through body, angle body, T-body
- Flow Range: Cv 0.34 to 21
- Seal Class: Class IV (metal-to-metal)
- Kimray's process of lapping the ball of the trim against the seat creates that very tight seal. The metal-to-metal seat is best for abrasive or erosive environments.
- Ideal For: Low flow and/or abrasive conditions
Even though they’re called “high pressure” valves, you don’t have to use them only in high-pressure systems. Stem-guided HPCVs often perform exceptionally well in low-pressure precision control applications.
Trim and Port Options
Cage Guided: Full Port or Reduced Port
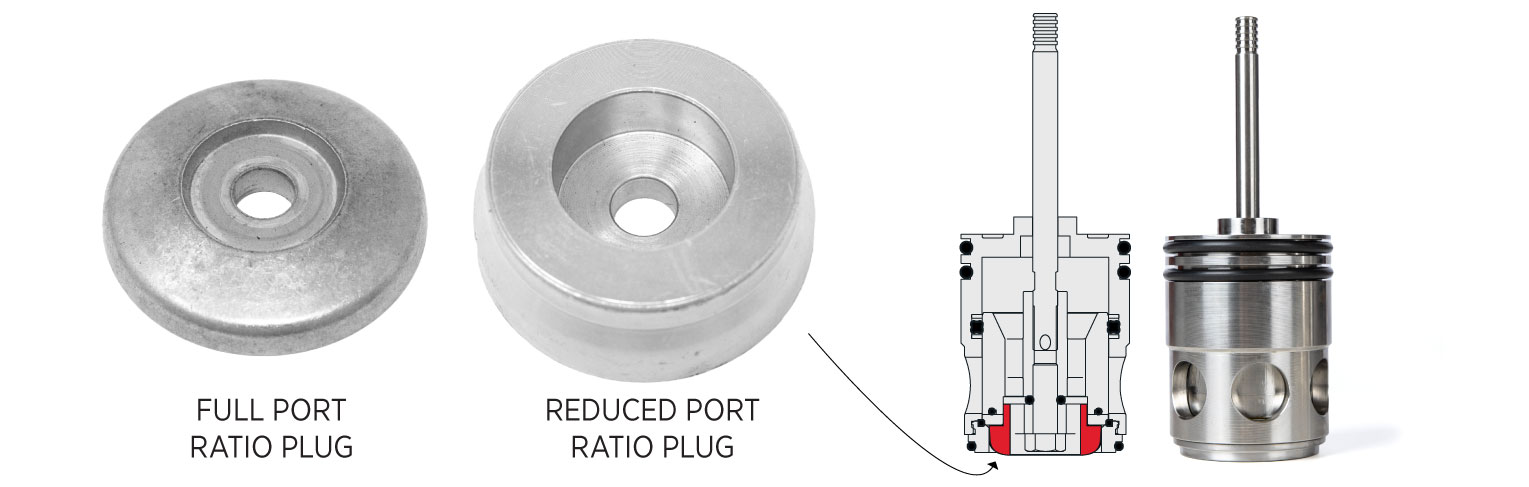
Cage guided HPCVs can be built as either full or reduced port or converted as needed.
- Full Port: Trim matches the inlet size—perfect for maximum flow.
- Reduced Port: Trim is typically half the inlet size—great for tighter control as production declines.
Switching between full and reduced port is simple. You can swap the trim or plug assembly without replacing the valve for an easy, cost-effective retrofit.
Convert Full Port or Reduced Port Plug Assembly Trim
Stem Guided: Trim Types & Applications
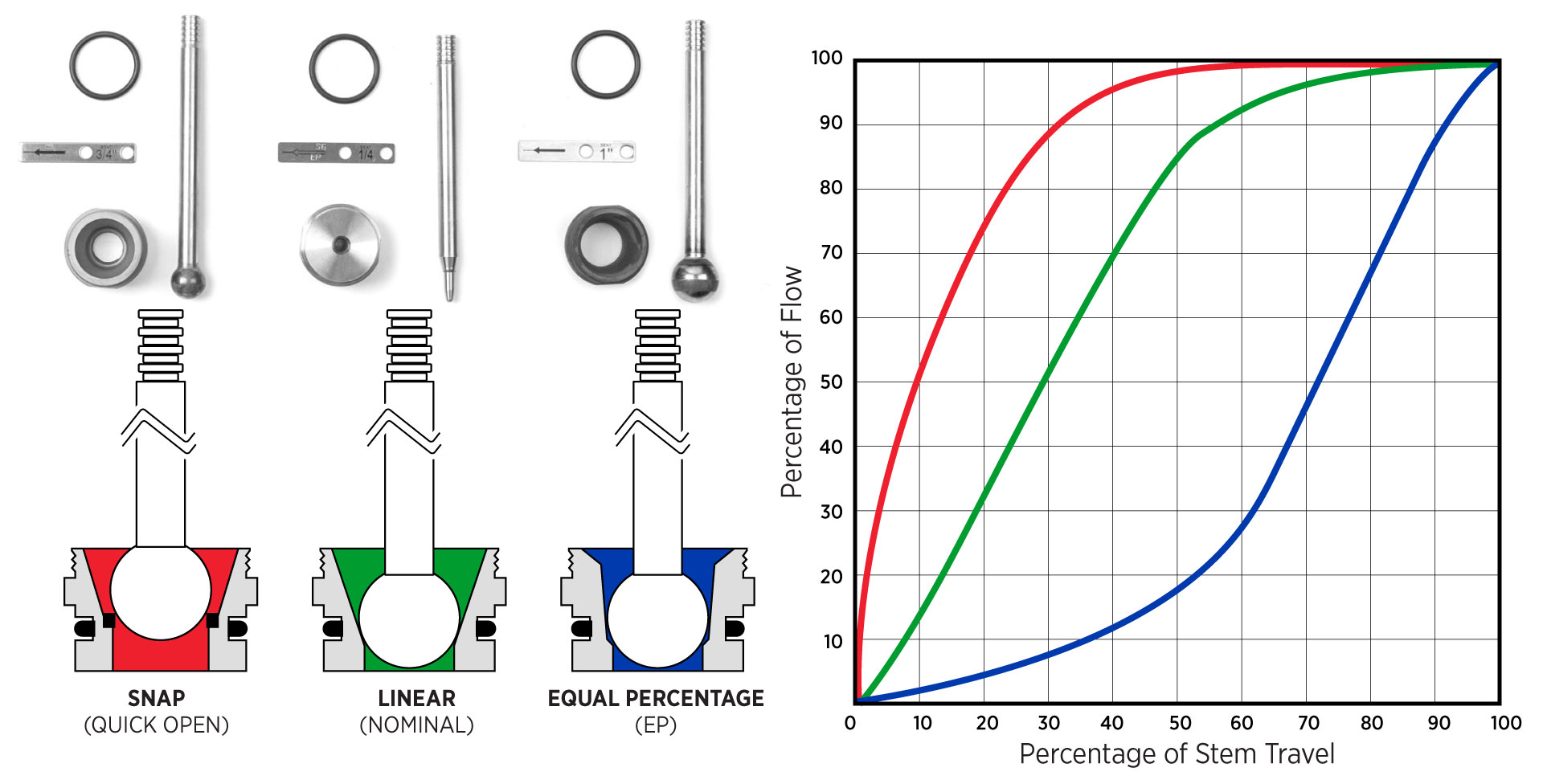
Stem guided HPCVs have a wide range of trim set sizes from 1/8" to 1". There are also three different types of trim depending on your application needs.
- Equal Percentage (EP): For smooth, precise control in pressure or flow applications. Cv increases gradually as the valve opens.
- Linear (Nominal): For standard liquid dump applications where flow increases proportionally with valve travel.
- Snap / Quick Opening (Carbide): For erosive or sandy applications. Provides fast, full opening to keep debris from wearing out internal components as quickly.
Control Valve Trim, Seats, and Springs
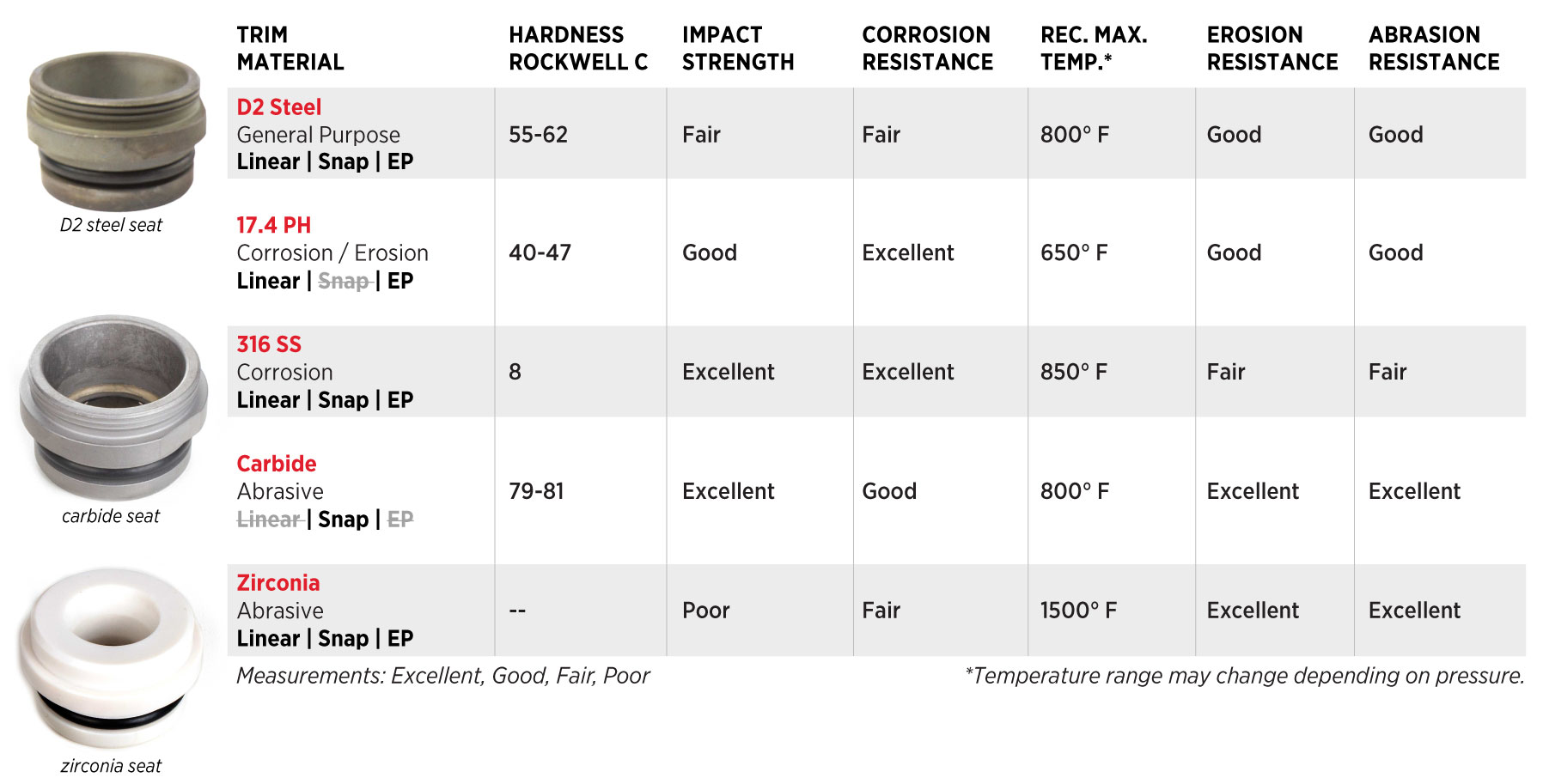
Material Options for Harsh Service
Kimray offers a range of materials and elastomers so you can tailor your HPCV to the environment:
- Standard Service: Hardened D2 steel for general purpose applications.
- Sour Gas or Corrosive Service: 316 stainless steel trims for corrosion resistance.
- Dual Protection: 17-4 PH, combining erosion and corrosion resistance.
- Severe Erosive Service: Carbide or zirconia trims (also consider combining with a T-body designs with replaceable wear plugs to absorb abrasive flow.)
More About Control Valve Trims & Seats
.jpg)
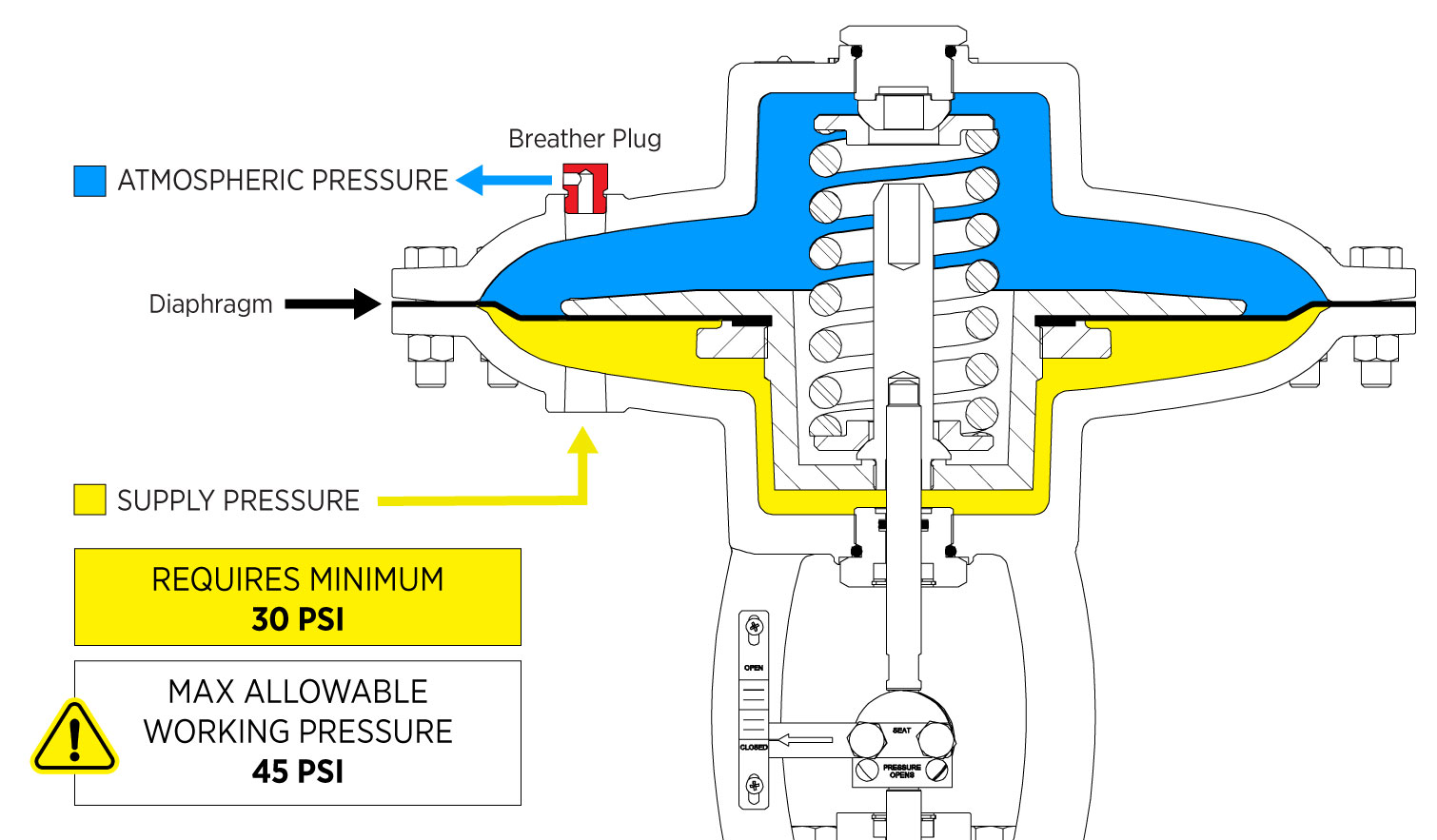
Actuation & Crack Pressure
All Kimray HPCVs use 30 PSI actuator pressure, no matter if your supply gas is compressed air, nitrogen, or natural gas. The maximum working pressure is 45 PSI. Exceeding that limit can damage the diaphragm and cause continuous venting.
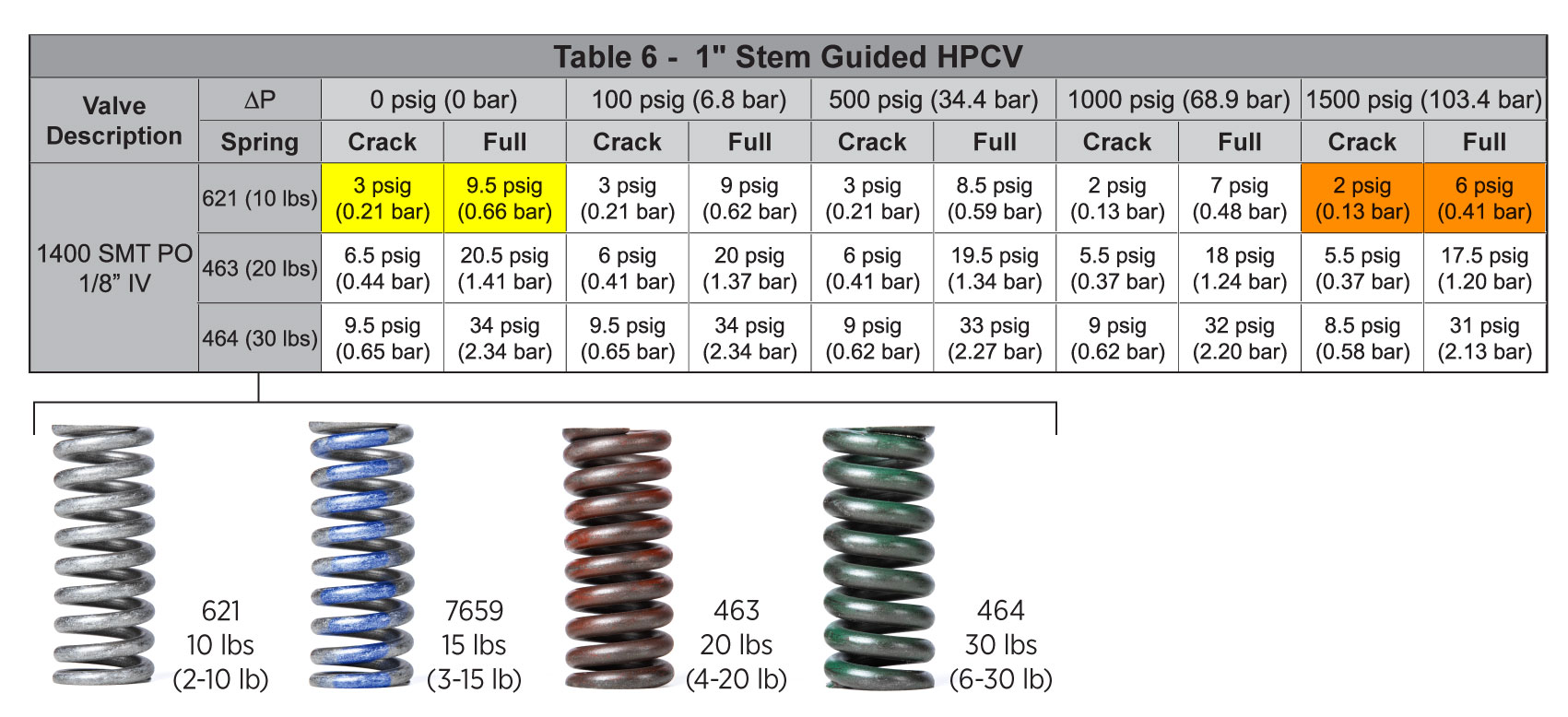
Crack pressure is the point where the valve just starts to open. It depends on the pressure differential across the valve and the spring in your actuator. For example, a 1-inch valve with a 10-lb spring will begin to crack open around 2 PSI and be fully open near 6 PSI, depending on conditions.
Electric Actuation
The pneumatic actuator on high pressure control valves can be swapped for electric actuation–either the Kimray Electric Actuator or one of our partner products–the Valvcon or Tritex II.
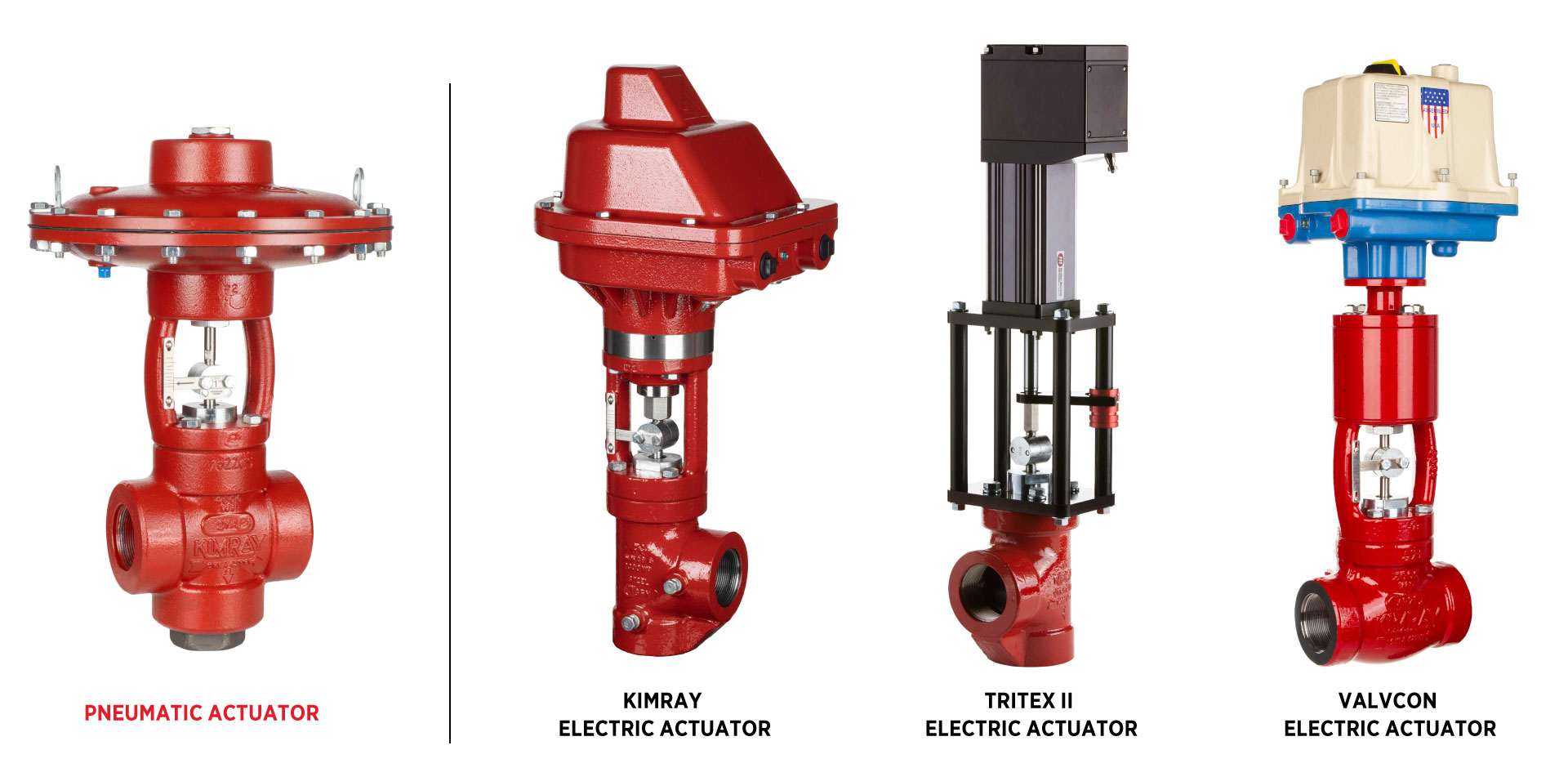
Electric actuators enable full automation and integration with electrical control systems for pressure, flow, or temperature management.
Electric Actuator for Pressure Regulation Electric Actuator for Dump Applications
HPCV Packages & Other Models
Pressure Regulation Valve Package
A high pressure control valve package includes a pressure pilot (such as the 30 HPG), a drip pot, a supply gas regulator (reducing to 30 psi), and a sense line protector to prevent overpressure.
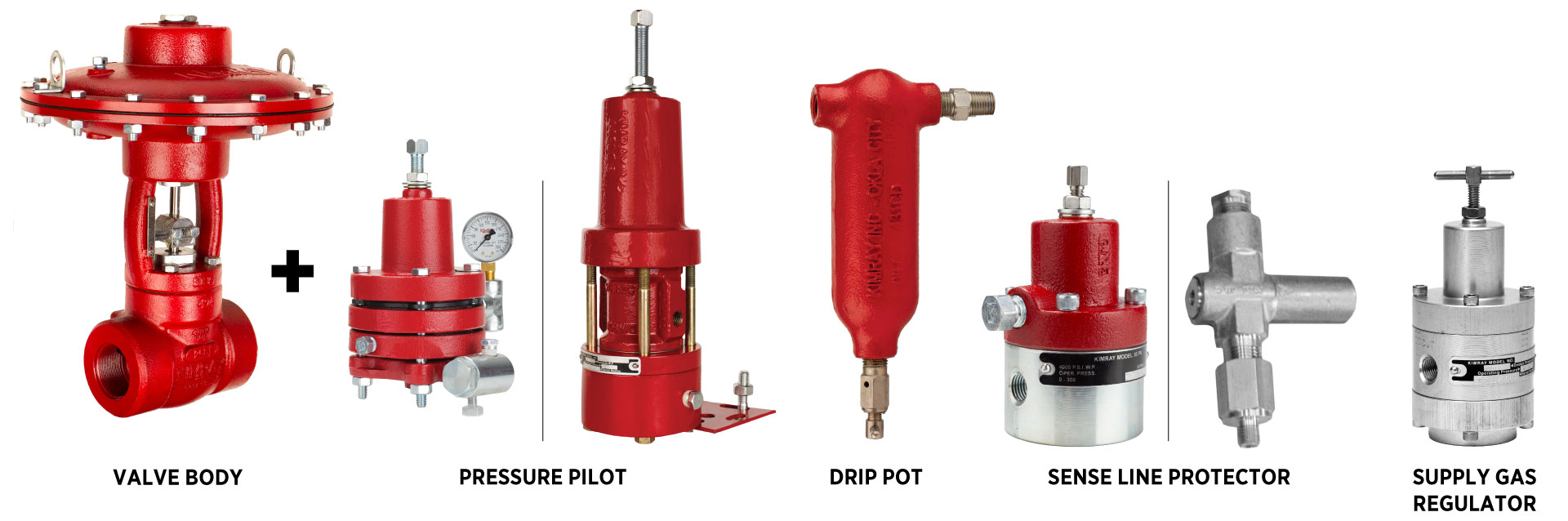
High Pressure Control Valve Packages Overview
BP Package AnimationPR Package Animation
Pressure Gap Control Package (High/Low)
A high/low package uses two pilots to keep a valve open between two pressure set points. If pressure rises above or falls below that range, the valve closes. This setup is often used on gas lift wellheads.
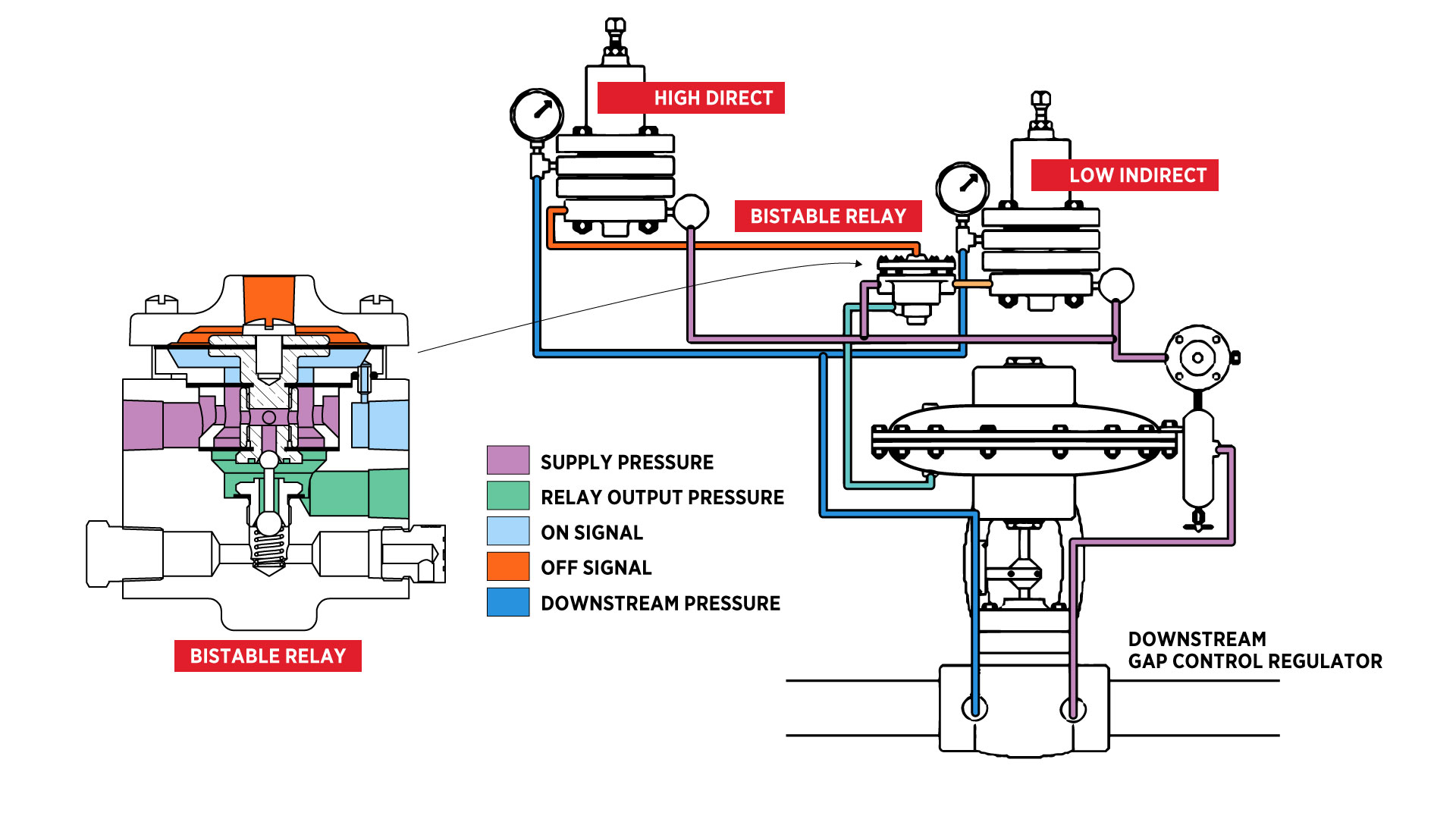
It controls the valve to stays open as long as the sensed pressure is between two set points. One pilot will be a lower set point and a second pilot will be the high set point. As long as the pressure stays between the two set points, the valve remains open.
A typical application would be for a gas lift wellhead to remain open as long as it's between two set points. If it gets lower, you want the well to be closed in to build pressure. If it gets too high and it's going to overpressure equipment, you want that valve to close.
Pneumatic Relay for Pressure Gap Control
Non-Freeze Dump Valve
The non-freeze dump valve uses vessel heat to prevent freezing caused by large pressure drops (Joule-Thomson effect). It’s typically used on gas production units and condensate vessels.
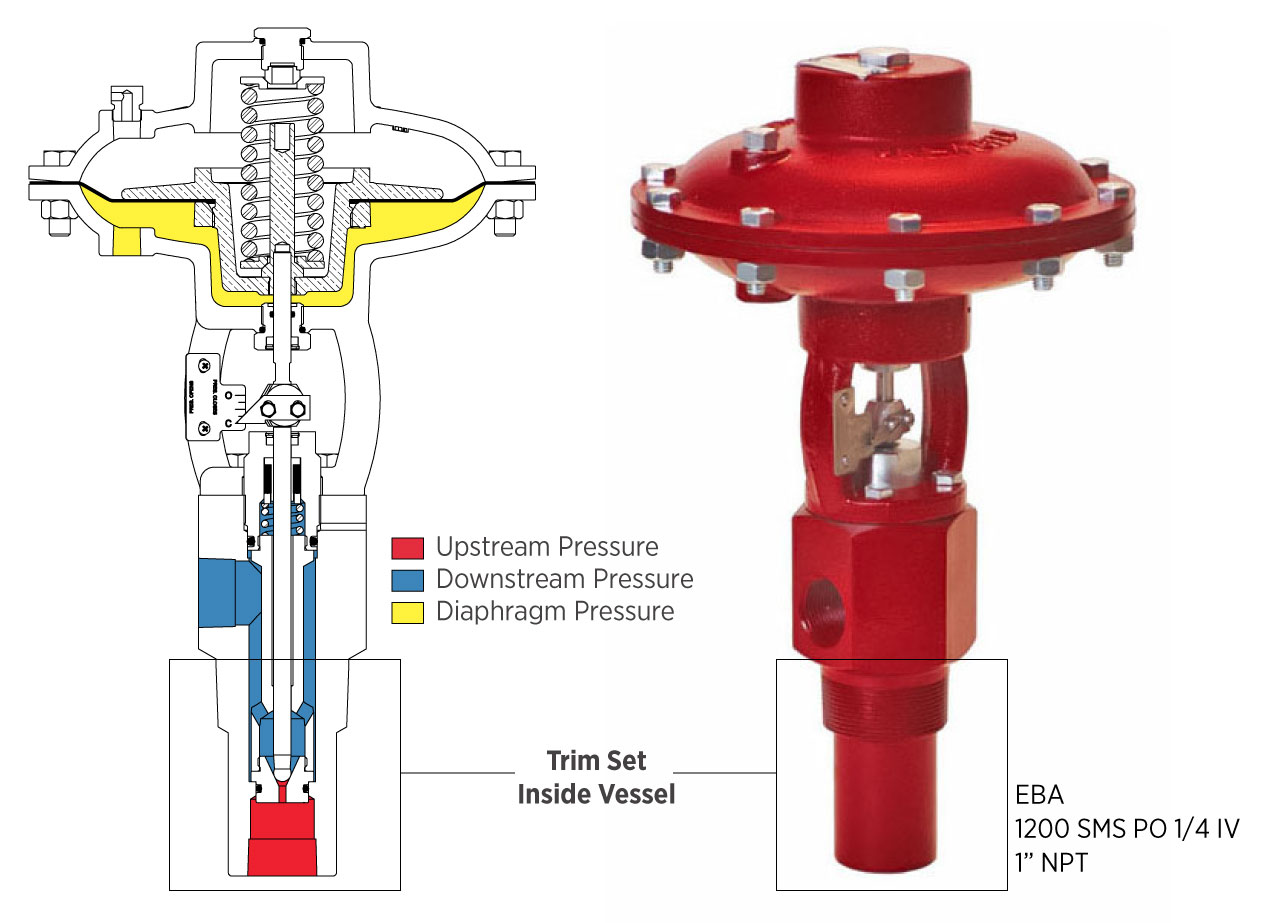
Large pressure drops and consequently large temperature loss, can introduce freezing problems. The non freeze valve trim set is inside the vessel utilizing vessel heat and shielded from ambient cold temperatures. Typical applications include gas production units for dump valves.
They're typically installed on top of the vessel using an installed stinger to reach down to the liquid level inside of the vessel.
Metering Valves
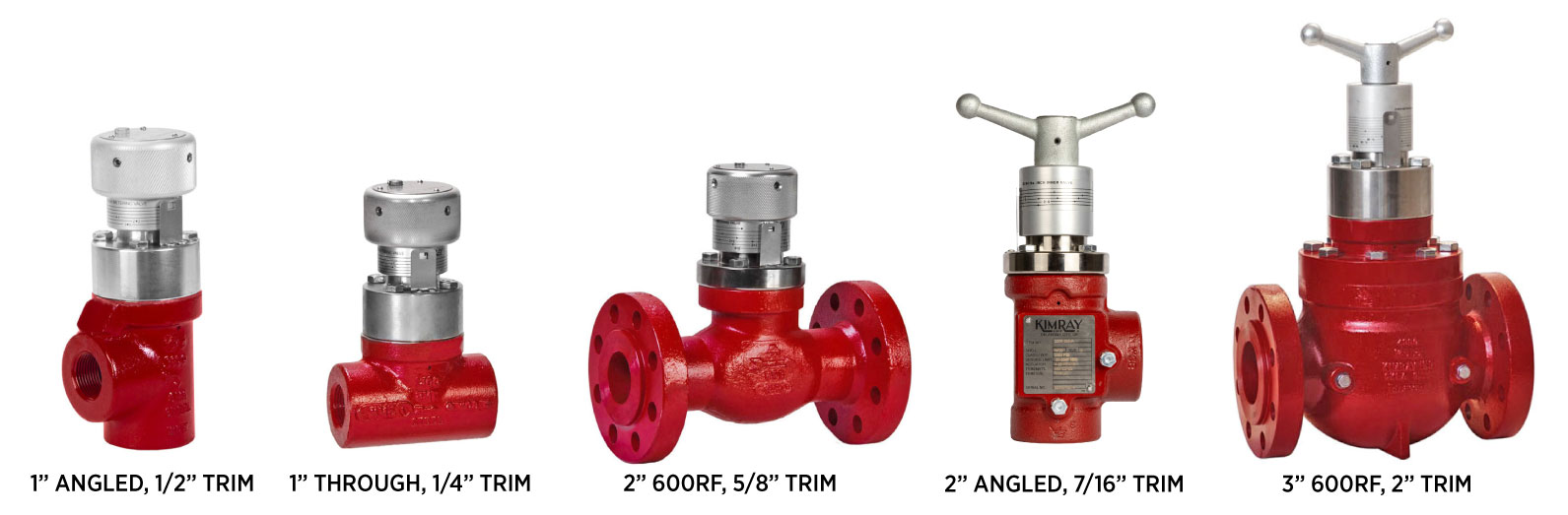

Metering valves are manual versions of high pressure control valves, allowing fixed-position operation for pressure cuts or choking. They can be used in applications where you do not need the control valve to change positions on its own but want the valve to go a certain percentage open and remain there. You can do this for initial pressure cuts or other pressure choking applications.
Metering Valves | Kimray Product Overview
T-Body
The T-body design helps mitigate erosion by using a replaceable wear plug made of hardened material. This wear plug takes the brunt of the damage from erosives and can easily be replaced. It can be used in both angle and through-body applications.
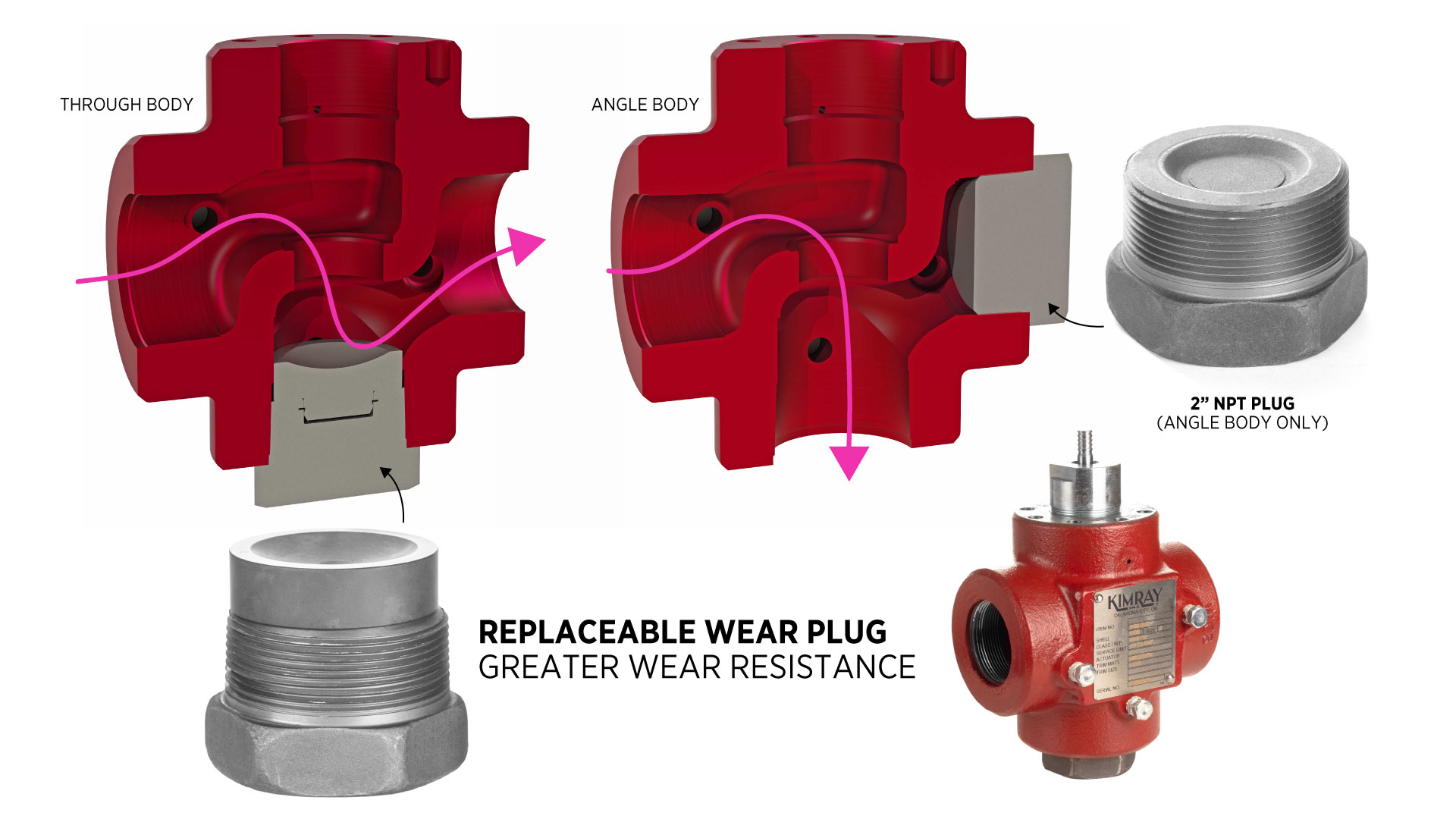
How a T-Body High Pressure Control Valve Works
Three-Way and Splitter Valves
Three-way or splitter valves can divert flow between processes—such as routing cooled fluid to a heater when temperature drops below a set point.
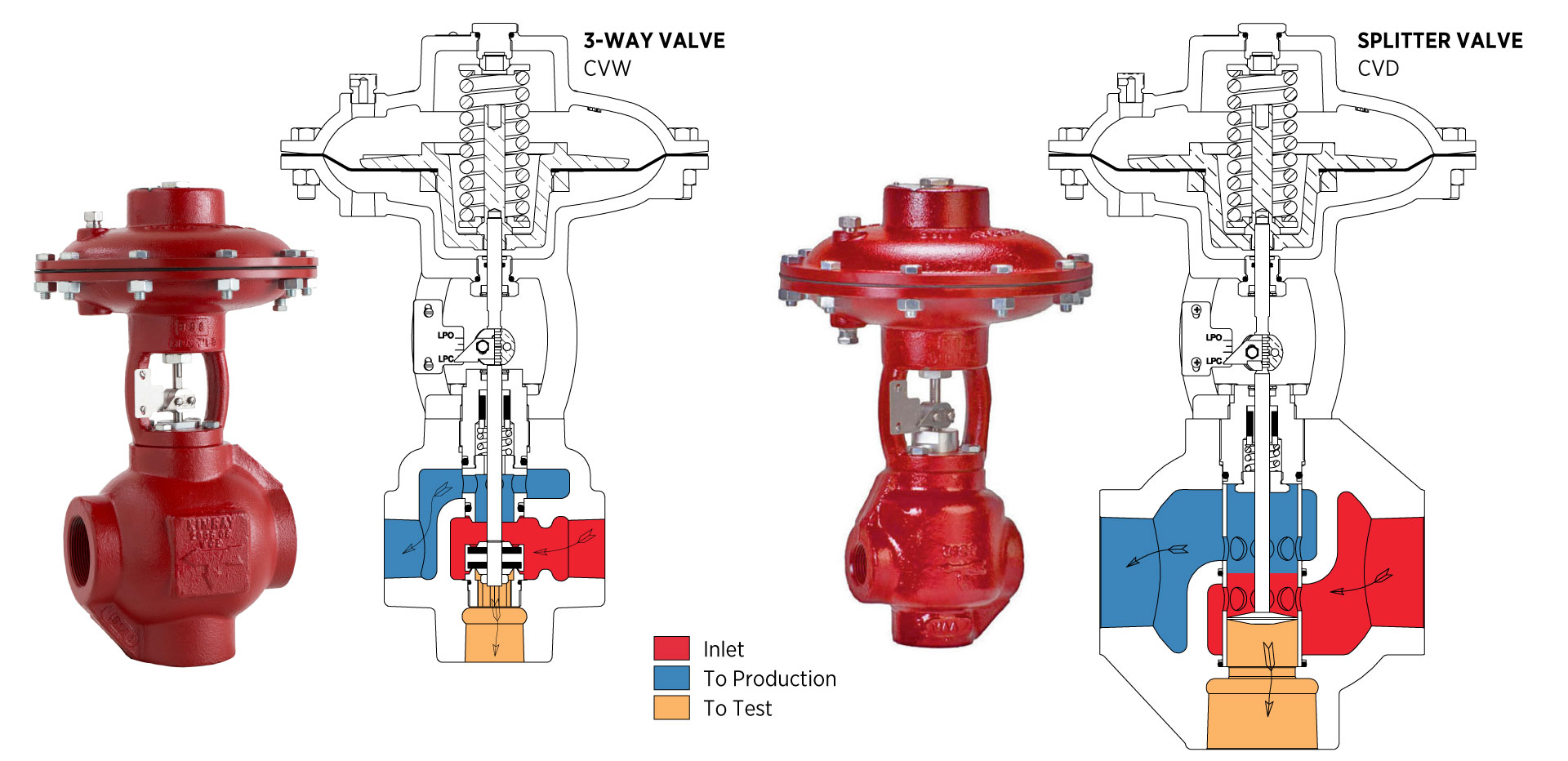
These can also be used in fluid temperature control–if a fluid temperature drops below a certain temperature, it's diverted to a heater. If it meets that temperature requirement, it diverts the flow to a different process.
Maintenance Tips
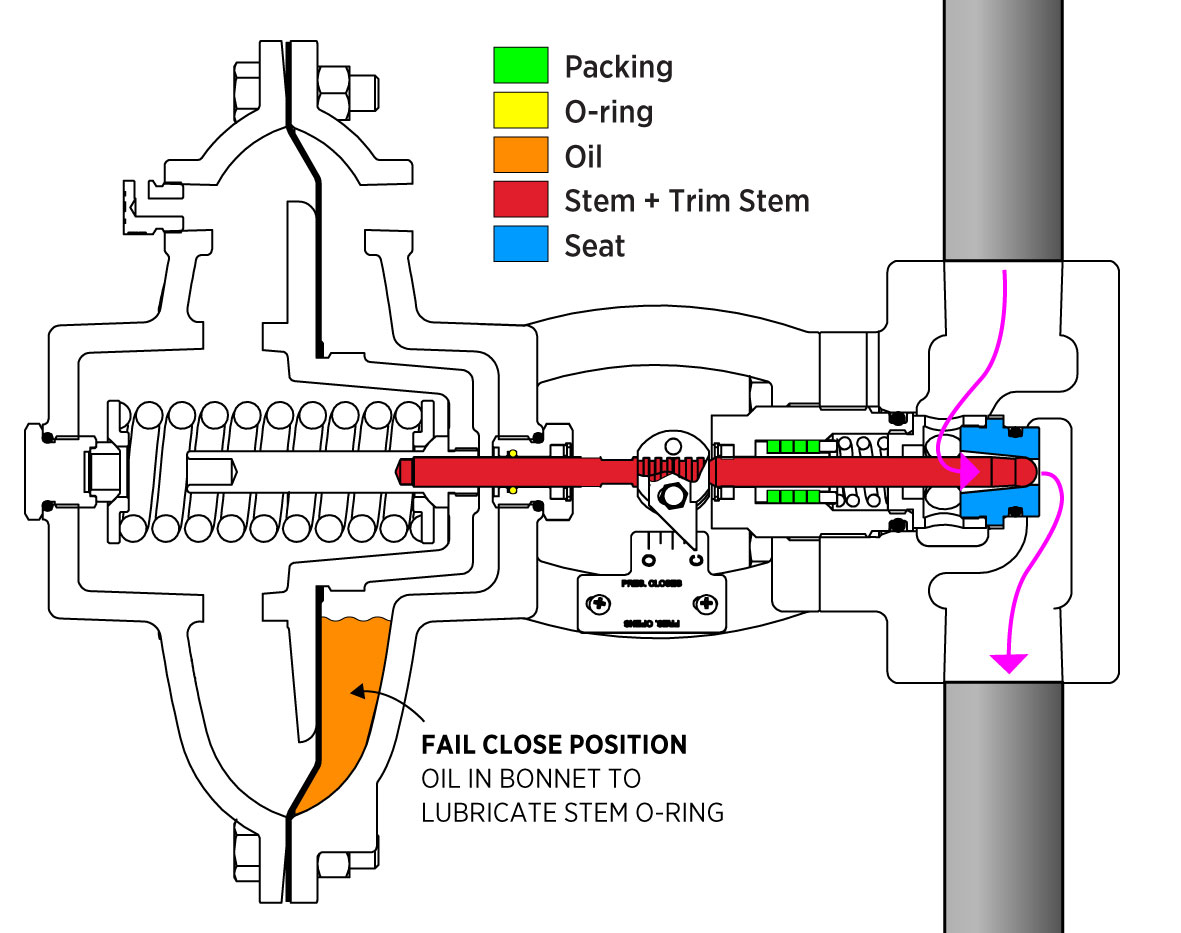
- Keep the actuator oil level above the small communication hole in order to lubricate the O-ring.
- Avoid mounting valves sideways if possible. It causes uneven packing wear and early failure.
- High pressure control valves can be mounted on their side, but doing so can cause uneven packing wear and prevent proper O-ring lubrication, especially in larger valves.
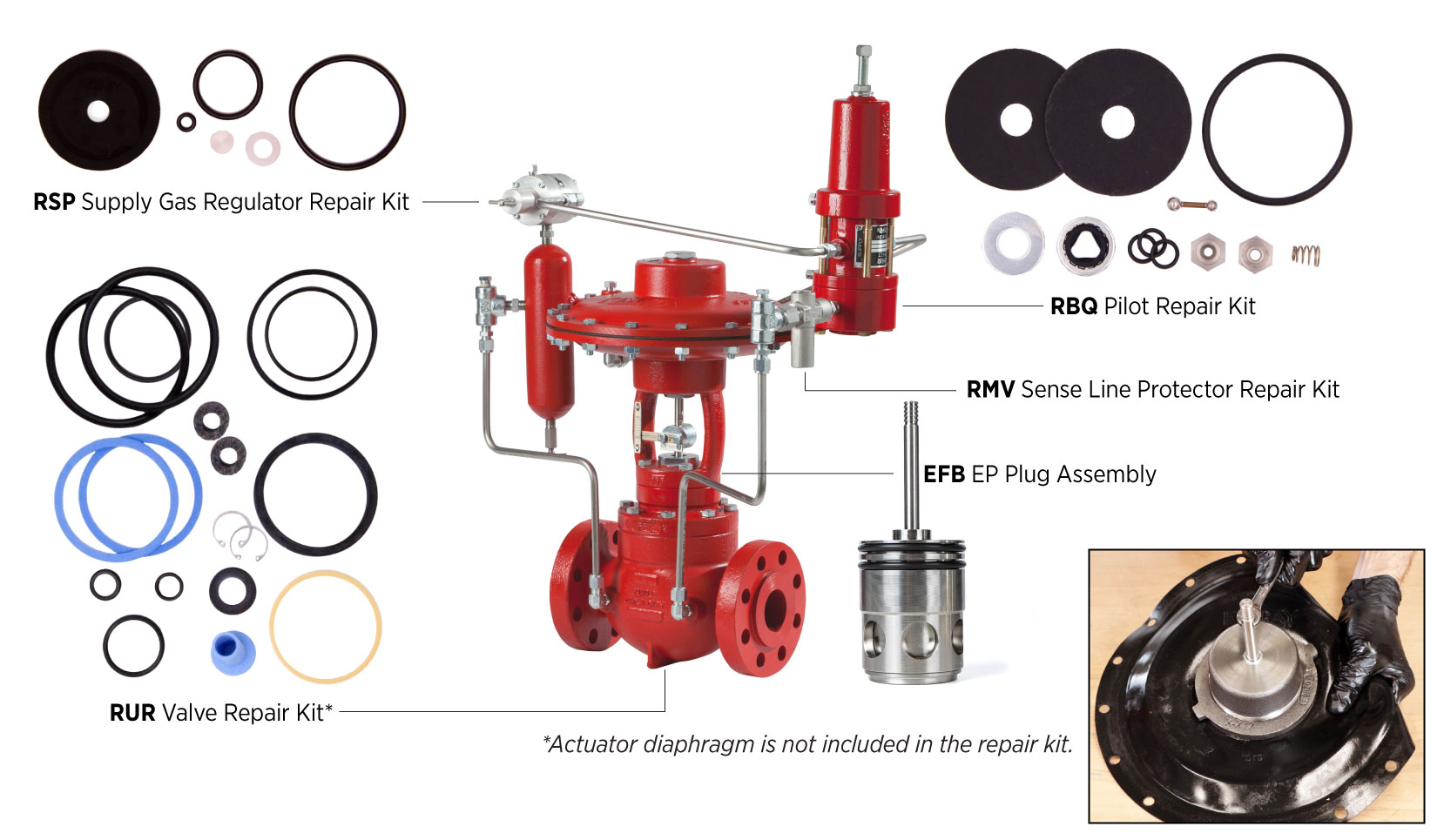
- Use Kimray repair kits for quick in-line maintenance without removing the valve body.
Stem Guided Repair Video Cage Guided Repair Video
Whether you’re regulating pressure, dumping liquids, or controlling temperature, Kimray HPCVs offer the flexibility, durability, and material options to fit your operation perfectly.
To learn more or schedule in-person training, visit the Kimray Training Page or contact your local Kimray store or authorized distributor.









































