Pneumatic relays are commonly used to switch air signals from one source to another, supply pressure to or exhaust pressure from a particular line or control device, or to initiate a control function.
In this video, Kyle shows you 4 common oil and gas applications for a pneumatic relay.
4 Applications for Pneumatic Relay
1. Signal booster
In a signal booster application, a relay is used to boost the output pressure of a control device, like a pilot.
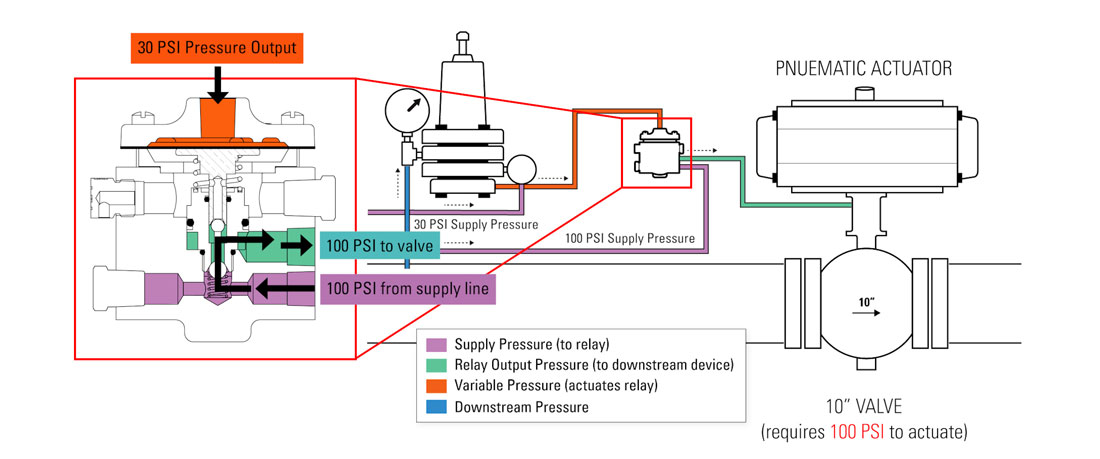
For example, imagine a pneumatic actuator on a large valve that requires 100 PSI to actuate.
A pressure pilot is monitoring conditions upstream of the valve through a sense line. However, the pilot has a maximum output of 30 PSI, well under the 100 PSI required to actuate the large valve.
So, when the pilot reaches its set point, it sends its pressure output of 30 PSI to the relay via the variable pressure line.
The relay then responds by sending 100 PSI from a separate supply line through its output to the large valve actuator so it can open.
2. Indirect Shut-in
A second application for a pneumatic relay is for indirect shut-in. Indirect shut-in refers to either a pressure- or temperature-controlled system that is shut-in when there is an upset so the process does not continue until manually reset.
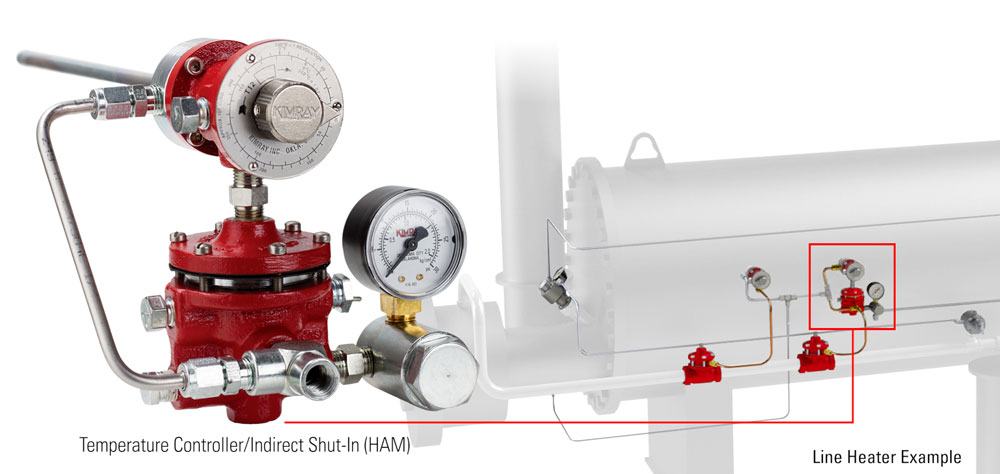

In a temperature-controlled system, an indirect shut-in uses a relay to shut down a process to prevent damage to equipment in the event that the TEMPERATURE goes over its set point.
These can be used in heaters, emulsion treaters, reboilers, steam generators, heat exchangers and salt bath heaters.
In a pressure-controlled system, an indirect shut-in uses a relay to shut down a process to prevent damage to equipment in the event that the PRESSURE goes over its set point.
These can be used in separators, knockouts, and other pressurized vessels.
3. Pressure Gap Control
If you need to pneumatically control a pressure range or gap, you can use the bistable pneumatic relay with two pneumatic pilots. The pressure will fluctuate between the two set points of the pilots.
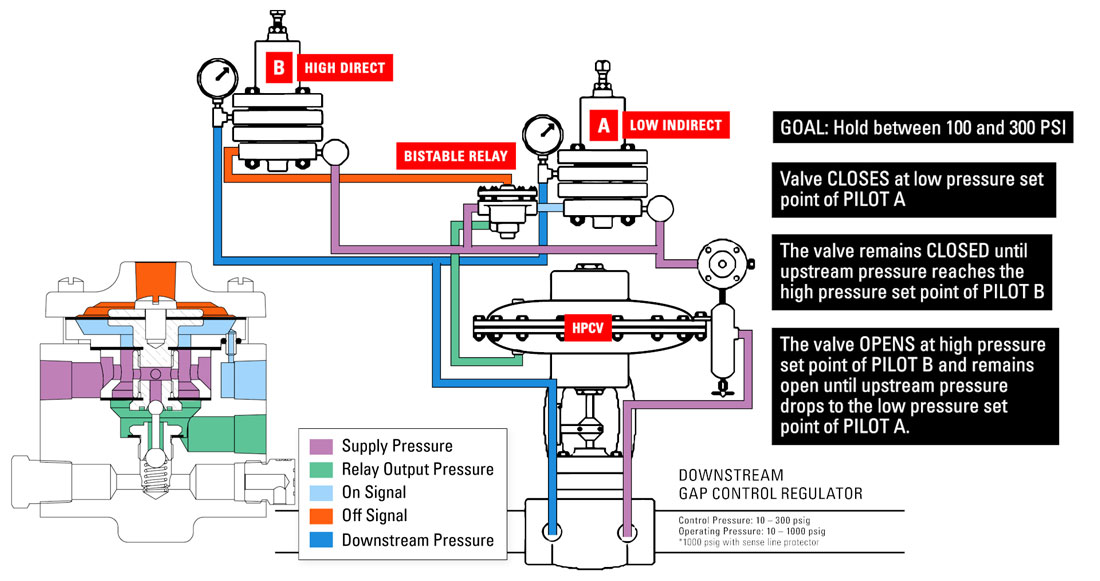
For example, say you want a high pressure control valve to hold pressures between 100 and 300 PSI.
- The high pressure control valve closes at the low pressure set point of pilot A.
- The valve remains closed until upstream pressure reaches the high pressure set point of pilot B.
- The valve opens at high pressure set point of pilot B and remains open until upstream pressure drops to the low pressure set point of pilot A.
One common application for the bistable pneumatic relay for pressure gap control in gas lift.
Instead of taxing the compressor by putting a specific pressure downhole, a producer can set a gap between 800 - 1000 PSI. They get good production with any pressure in between this gap.
4. Liquid Gap Control
You can also use the bistable pneumatic relay to help control a liquid level span.
To do this, you need two pneumatic pilots tubed to control valves and two level controllers, one set to direct acting and one to indirect acting.
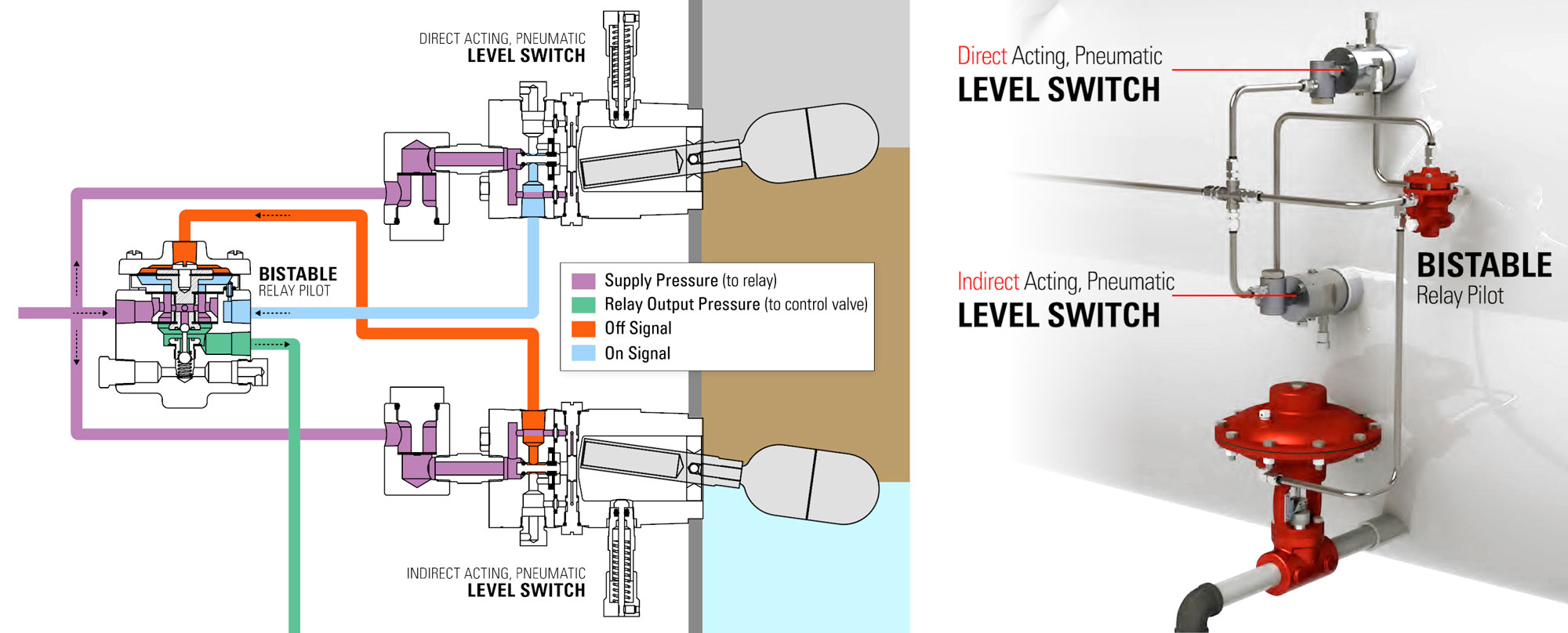
As the float on the high level, direct-acting pneumatic liquid level controller moves upward, a pneumatic output to the lower side of the main diaphragm in the bistable relay is created.
As the main diaphragm moves upward in the relay, the small ball on the pilot plug is unseated, allowing the supply pressure to signal the control valve to open.
As liquid level lowers on the low level indirect-acting liquid level controller, the float moves down, allowing the supply pressure to give the pneumatic “off” signal to the top of the bistable pilot. This overcomes the “on” signal and causes the control valve to close.
To speak with an expert about our relays or any other Kimray product, contact our Kimray applications team.









































