Valve Flow Coefficient (Cv) is a valve’s capacity for a liquid or gas to flow through it.
It is technically defined as “the volume of water at 60°F (in US gallons) that will flow through a valve per minute with a pressure drop of 1 psi across the valve.”

In simpler terms, the larger the opening in a valve, the larger the Cv. As a valve is opening, the Cv increases until the valve is fully open, where it reaches its highest possible Cv, or 100% open Cv.
Example of Valve Flow Coefficient (Cv)
Below is a Valve Cv chart showing flow curves for two different valves: a 2-inch and 3-inch Kimray back pressure regulator.
As the stem opens, the Cv increases.
The maximum Cv for the 2-inch regulator is 47, while the maximum for the 3-inch regulator is 117.
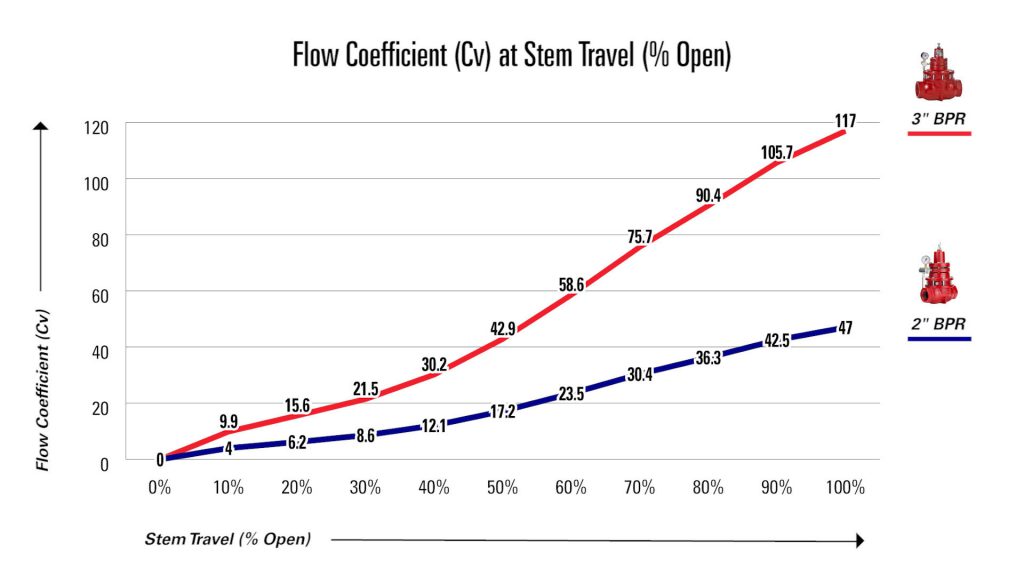
We recommend you select a valve for which the Cv falls between 20% and 80% open stem travel.
For example:
- If you used our valve sizing calculator and came up with a Cv value of 14, you would want to choose the 2-inch valve because in the 3-inch valve, 14 would fall outside of the recommended range.
- If you calculated a Cv value of 47, you would want to choose the 3-inch valve because in the 2-inch, 47 would fall outside of our recommended range.
- If you calculated a Cv of 35, it falls in the range for both valves. In this case we would recommend the 3-inch because it falls closer to the middle of the flow curve.
How to Size a Control Valve
The first question you need to ask when valve sizing is “What is my pressure?”
- For GAS applications, if your pressure is MORE than 300psi, you need a high pressure control valve;
if it’s LESS than 300 psi, you can likely use a low pressure regulator. - For LIQUID applications, if your pressure is MORE than 500psi, you need a high pressure control valve;
if it’s LESS than 500 psi, you can use a lever-operated or pneumatic dump valve.
While it sounds obvious to choose high pressure valve for high pressure application, there is another key factor you have to consider: Calculated Cv.
The Importance of Calculated Cv
The second question you need to ask when valve sizing is “What is my Cv?”
Again, Cv is the number of gallons of water that will pass through a given flow restriction at a 1 psi differential. You can think of it as the orifice size of a valve.
To calculate your Cv, plug your flow conditions into the Kimray Sizing Calculator. You can also use this video guide to learn how to use this sizing calculator.
Let’s look at two sizing examples.
Example 1
Your pressure is less than 300 psi and your required Cv is 3 or greater.
In this case, a low pressure regulator should work for a gas application, while a low pressure control valve or mechanical dump valve will work for a liquid application.
Example 2
Your pressure is still less than 300 psi, but your required Cv is less than 3.
In this example, you should use a Stem Guided High Pressure Control Valve because it can meet the small Cv requirements.
This may sound counter-intuitive to use a high pressure control valve for low pressure, so let’s dig a little further…
What Calculated Cv means for Valve Trim Sizes
Kimray low pressure valves and regulators come with 2 trim options—full port or reduced port—and might be too big for the small flow rates. Kimray 2” stem-guided high pressure control valves come with 9 trim options ranging from ¼” up to 1”. Our 1” stem-guided valve trim options range from 1/8” – ½”.
Stem-guided valves have small Cvs—from .34 to 21. They can handle low flow as well as high pressure drop applications where you have a small Cv requirement.
For larger Cvs and higher pressures, Kimray’s Cage Guided High Pressure Control Valves are full port valves with a Cv range of 28.6 to 1,091.
While our stem-guided valves are available only in 1” and 2” sizes, our cage-guided valves are available in 2" through 10".
Can I Change the Cv on a Control Valve?
We’ve now walked through selecting a new valve. But what about if you have valves on an existing well and conditions change?
A key benefit of Kimray high pressure control valves is their versatility.
For example, if you resize your valve with the new conditions and the calculated Cv does not fit the trim on your existing stem-guided valves, you can swap the trim for a different size. This will keep you from having to change your piping to fit a larger or smaller valve.
Converting Units to Size a Control Valve
Sometimes you will have these numbers in their appropriate units. Other times, however, you will need to perform some conversations to get them into the correct unit.
For example, you may know your flow rate in pounds per hour, but for the sizing tool you need a volume flow rate, such as gallons per minute.
In order to make these conversions easier, we have also created calculators preloaded with the appropriate formulas for converting these numbers. You can convert by entering your pounds per hour and the specific gravity, and the conversion tool will give you the flow rate in gallons per minute.
Download Liquid Conversion CalculatorDownload Gas Conversion Calculator











































