
NGLs are Natural Gas Liquids produced from an oil and gas well.
NGLs condense and fall out of the gas stream in pipelines or separation vessels due to a decrease in temperature, increase in pressure, or the scrubbing action that takes place inside the pipeline.
What is Natural Gas Composition?
Natural gas produced from a well contains many different resources that are separated at upstream and midstream gas production facilities.
These products are valuable and can be sold and used for heat, cooking, fuel, and more.
In the chart below, you can see the different resources that make up natural gas.
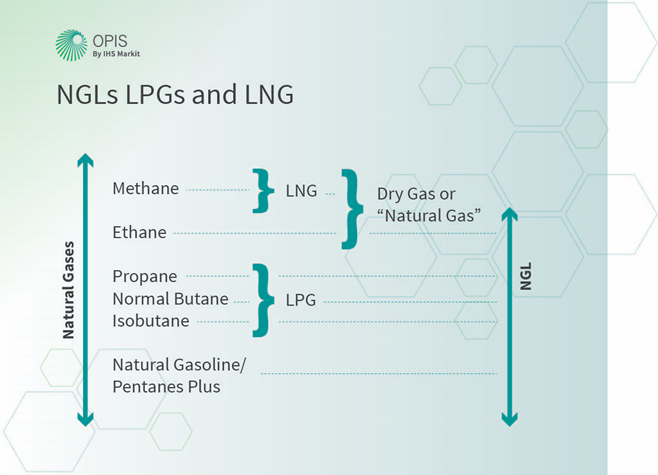
In addition to these resources, impurities can also be present in large proportions in natural gas, including:
- Carbon Dioxide
- Helium
- Nitrogen
- Hydrogen Sulfide
Producers and midstream companies must extract and dispose of these unwanted components during their production processes.
Two of the primary usable products produced are Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG) and Liquid Natural Gas (LNG).
How are NGLs Produced?
As mentioned above, raw natural gas contains many different resources. In order to isolate these resources, including NGLs, gas companies must “crack” the gasses.
Cracking gasses is a general term that means breaking various elements out of the natural gas we extract from below ground.
Processing plants run natural gas through a series of tanks designed to separate impurities, water, and natural gas liquids, or NGLs. They extract NGLs using a few primary methods:
- Compression, which adds pressure to gas, causing the liquids to fall out (natural gasoline or “drip gas”)
- Cryogenic expansion, which separates methane from the other components by freezing them
- Fractionation, which heats the elements and separates them using their different boiling points
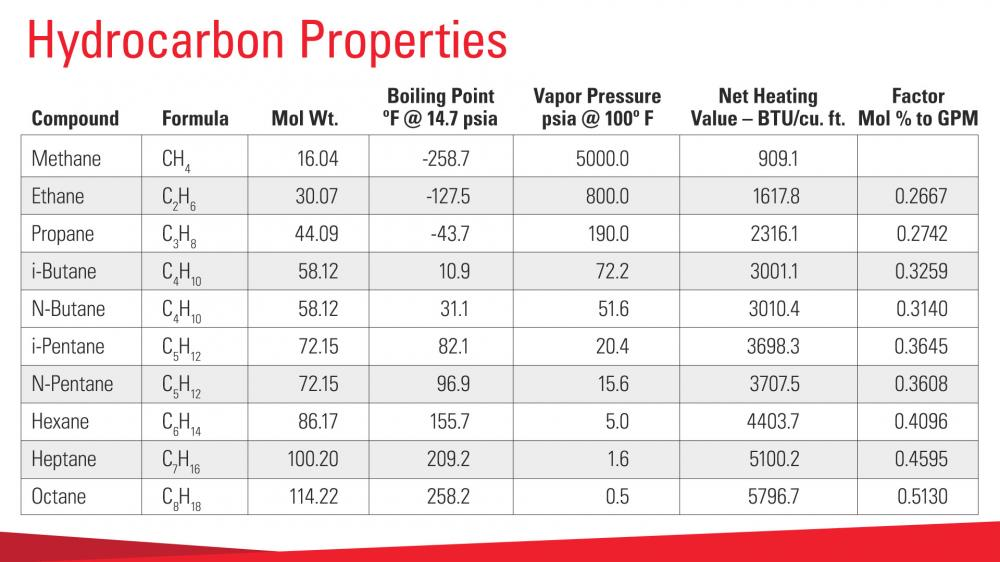
As you can see from the chart below, at a given dew point, a specific resource will condense and fall out of the gas.
Read: What is Hydrocarbon Dew Point?
What is the Difference Between NGL and Natural Gas?
Natural Gas is a raw, multi-faceted resource that must be cracked into various specific elements for consumer use.
NGLs are heavy hydrocarbon compounds with much higher dew points than methane and ethane gases (dry natural gas). These NGLs condense into liquids at higher temperatures than dry natural gas (methane & ethane).
What is the Difference Between LNG and NGL?
Liquified Natural Gas, abbreviated LNG, is a type of Natural Gas Liquid (NGL).
LNG is made primarily of methane. By adjusting the temperature of the methane to its hydrocarbon dew point, refineries convert the gas to liquid so it is easier to transport and sell. At ambient pressure, the LNG will be at temperatures approximately –256° F.
LNG is used when a pipeline is not available to get the gas to market. It is increasingly common in offshore and developing regions.
What is the Difference Between LPG and LNG?
Liquified Petroleum Gas, abbreviated LPG, is another type of Natural Gas Liquid (NGL).
LPG is made up of Propane and Butanes. Refineries liquify this gas at low temperatures (between -43° and 31° F).
LPG is typically used for heating and cooking and is commonly called “bottled gas.”
While LPG is considered a type of Natural Gas Liquid, Pentanes Plus are pure NGLs.








































