Hydrocarbon dew point—abbreviated HDP or HCDP—is a term unfamiliar to many oil and gas producers, but it has a significant effect on the processes in our industry.
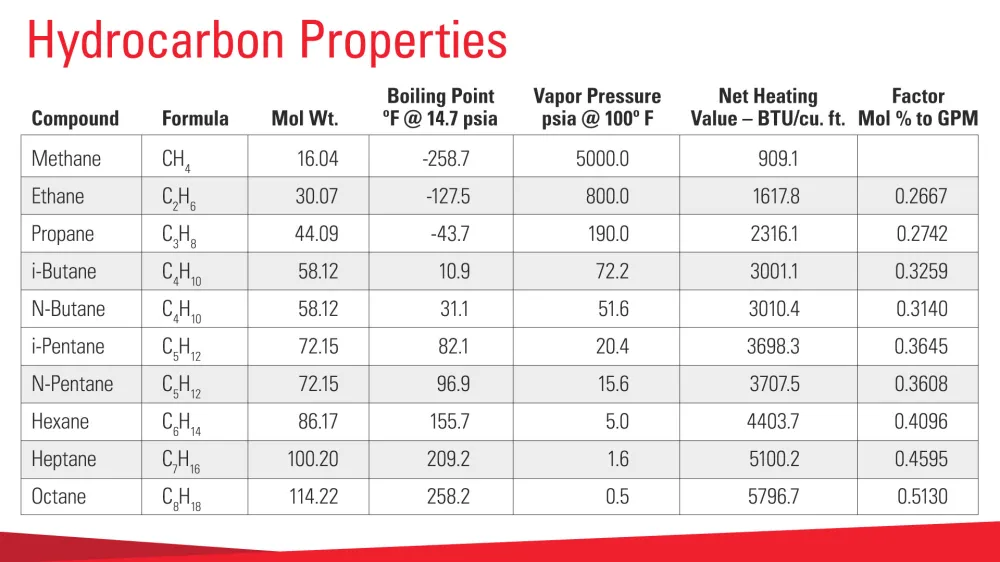
Hydrocarbon dew point is the temperature at which the hydrocarbon components of a natural gas begin to condense out of the gaseous phase into a liquid phase.
The maximum temperature at which such condensation takes place is called the "cricondentherm."
HCDP is a function of the gas composition as well as the pressure. It is used in the natural gas industry as a quality parameter. It will be specified in the contract from producers through processing, transmission and distribution companies to the end users.
The hydrocarbon dew point of a gas is a different concept from the water dew point, the latter being the temperature (at a given pressure) at which water vapor present in a gas mixture will condense out of the gas.
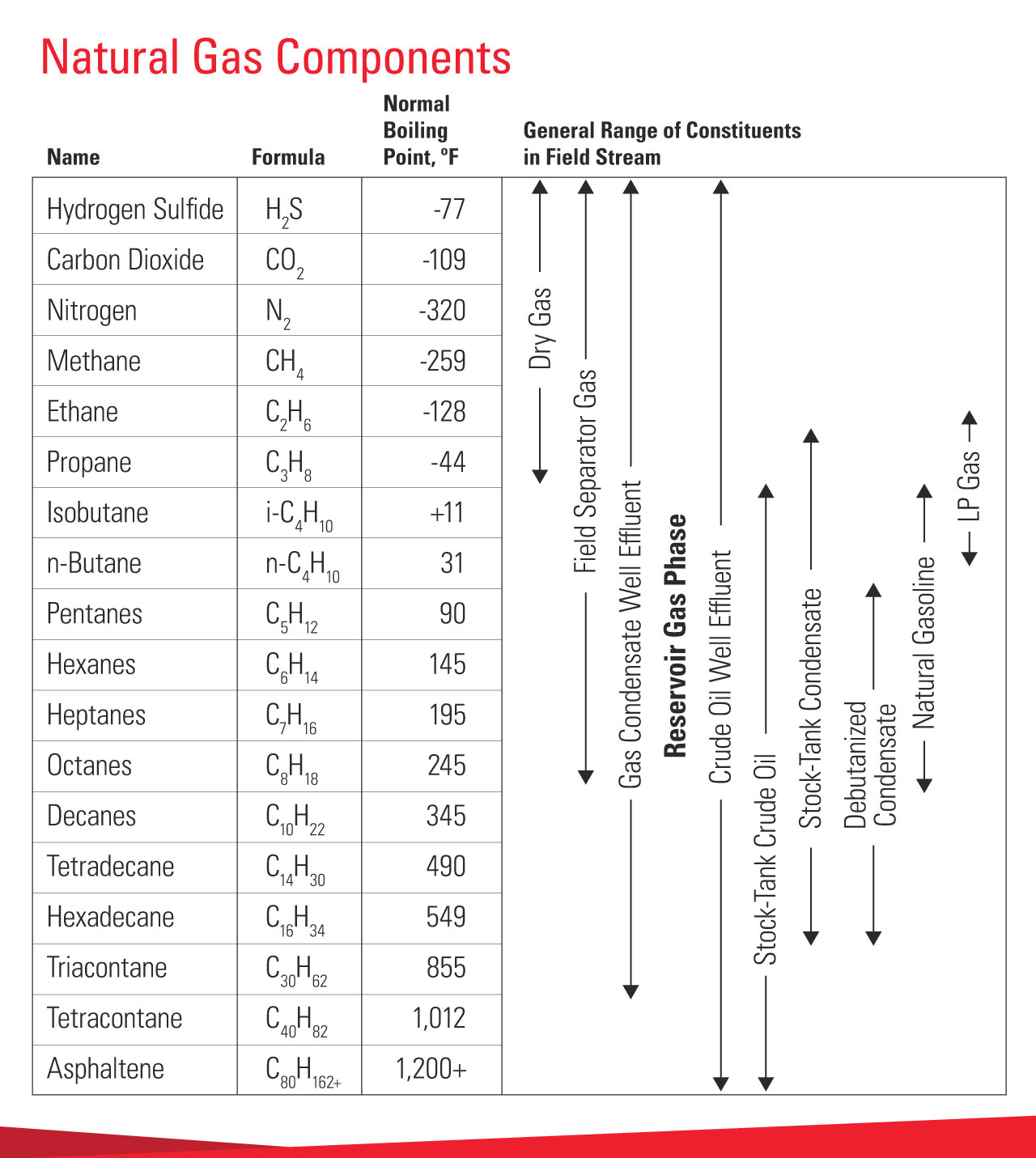
In gas dehydration, the water dew point is also impacted by temperature and pressure, and the gas is dehydrated to meet contract specifications and other safety requirements.
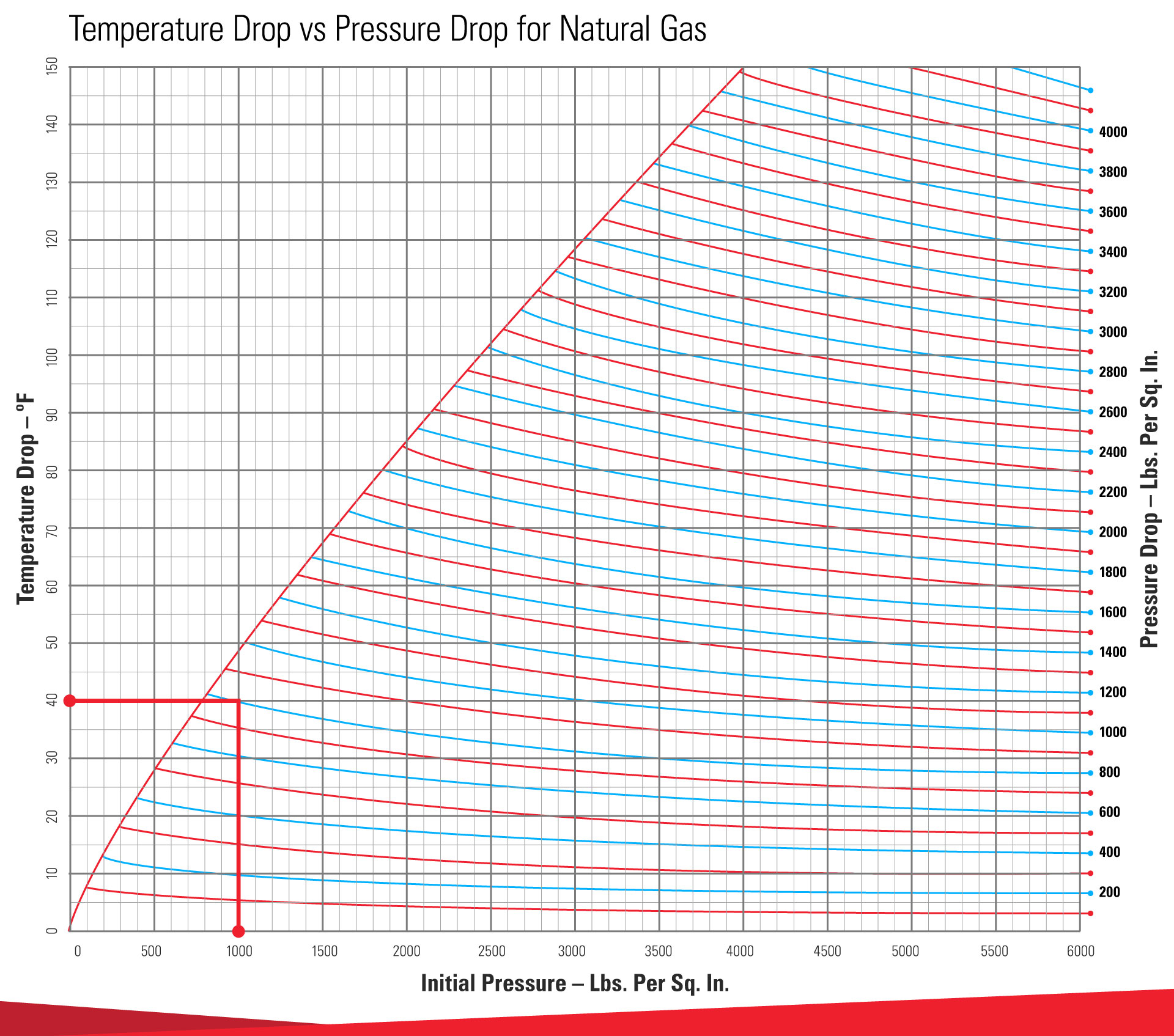
Hydrocarbon Dew Point Measurement
There are two primary methods of determining hydrocarbon dew point: theoretical method, and experimental method.
1. Theoretical Method
The theoretical method uses the component analysis of the gas mixture (usually via gas chromatography, GC) and then use an equation of state (EOS) to calculate what the dew point of the mixture should be at a given pressure.
2. Experimental Method
In the experimental method, one cools a surface on which gas condenses and then measures the temperature at which the condensation takes place
The theoretical method is more commonly used. Remember HCDP is the temperature and pressure at which we make liquids.
To speak with an expert about how hydrocarbon dew point affects your operation, contact your local Kimray store or authorized distributor.









































