Oil and gas electrical training can lead to gains in efficiency, safety, and environmental areas.
While historically oil and gas control products have been powered by mechanical and pneumatic means, a growing number of producers are incorporating the use of electric power.
The advantages of using electric products in the oilfield are significant, and include:
- increased efficiency
- decreased potential for hazardous situations
- remote monitoring and communication for production equipment and instrumentation
- decreased emissions
This growing trend has led to the increased need for oilfield electrician training and general information about how to use oilfield electric products.
Oil and Gas Electrical Training OUTLINE
In the Oil and Gas Electrical Training video above, Kimray Product Manager (and licensed electrician) Alex Crow introduces you to some basic electricity concepts—from how it is generated to common terms like amperage, volts, current and AC/DC.
The goal of this session is to get you feeling more comfortable with discussing and working with electric products in the field.
The Basics of Electric Power Generation
Power is not actually "generated," but is harnessed at a power plant. The term generation is somewhat misleading as energy is changed from one form to another.
What are the Two Types of Electrical Power Plants?
There are two main types of power plants: natural gas and coal.
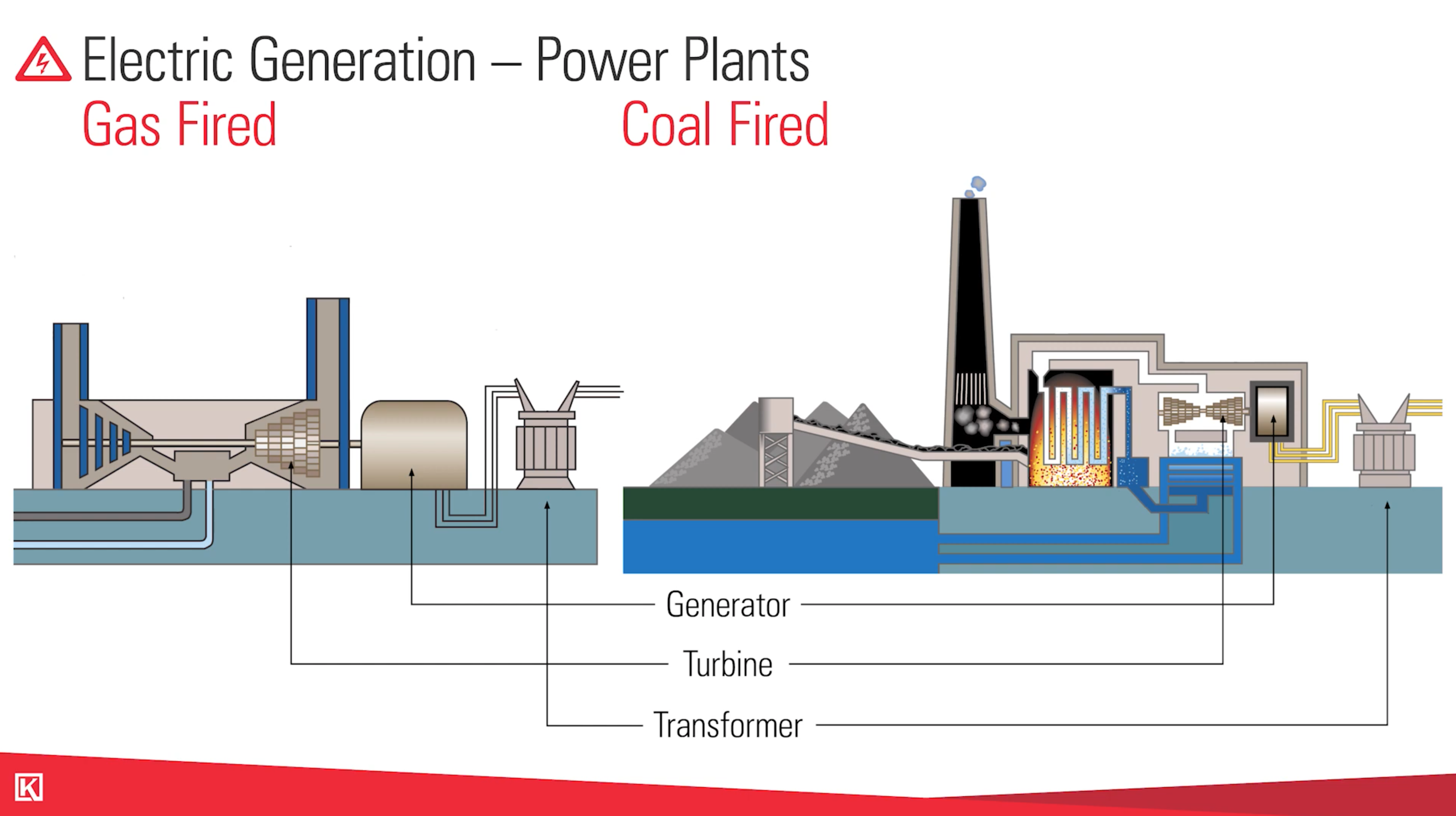
How Does a Natural Gas Power Plant Work?
Natural gas power plants and coal power plants follow the same basic steps, with the only difference being the inlet and outlet.
In a natural gas power plant, you've got a natural gas line coming in. It will burn the gas into a combustion chamber, spin the turbine, and change the electricity into a generator and out through the transformer.
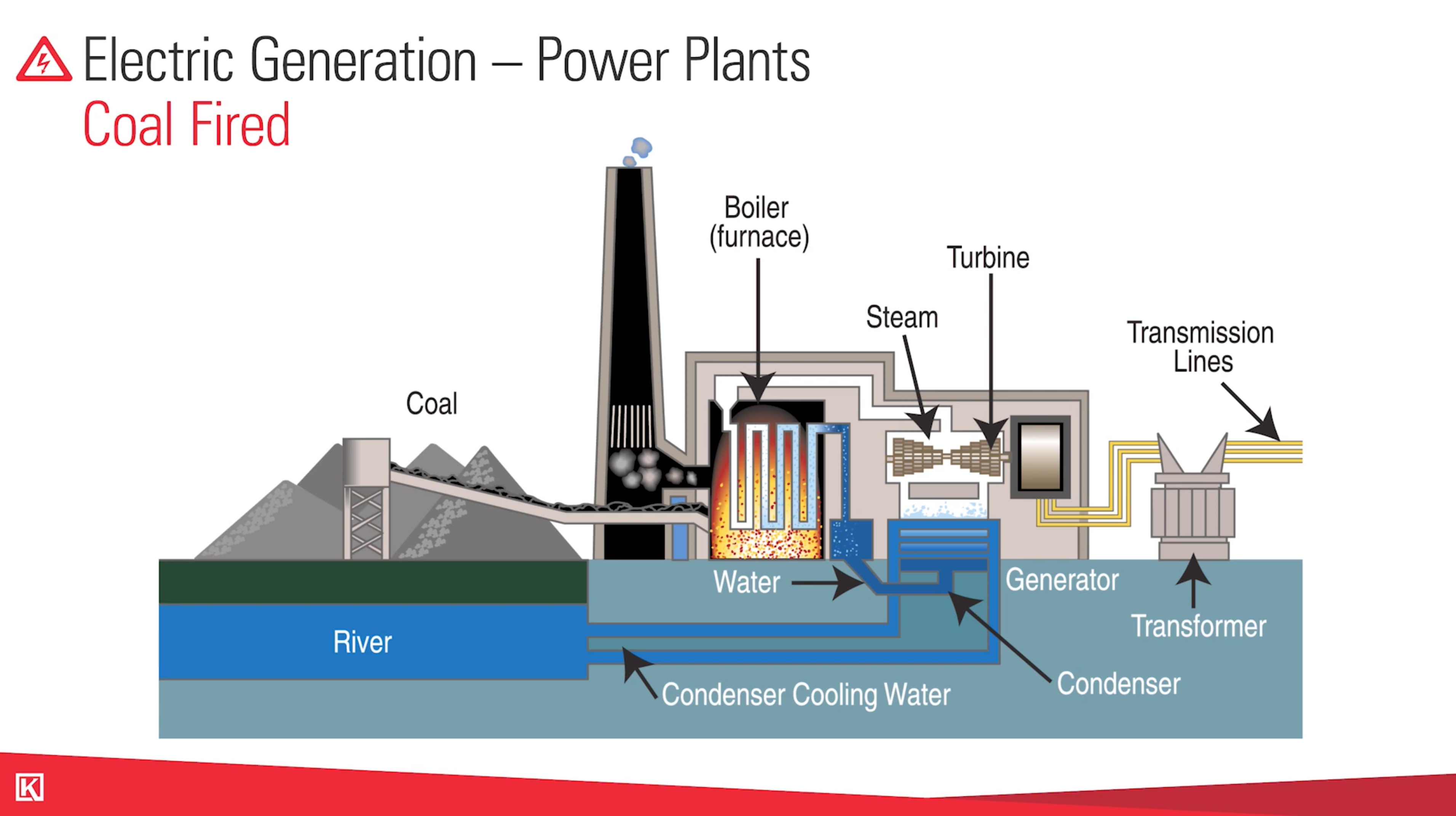
How Does a Coal Power Plant Work?
While in natural gas you have the power piped in, coal comes in through a rail or a truck offload.
From there, the same basic principles apply. The coal goes through a furnace, combusts into steam, spins the turbines, and goes out through the transmission lines.
Two non-conventional power plants are solar powered and wind powered.
How Does a Solar Power Plant Work?
Solar panels work by either harnessing heat or reflecting light and sending it to another power source.
Solar panels use a large storage tank of batteries, and from there the power goes into the turbine, out to the generator, and then out to the same utility lines.
A solar-thermal battery tank also has a mixture of the transformer and the generator on the inside.
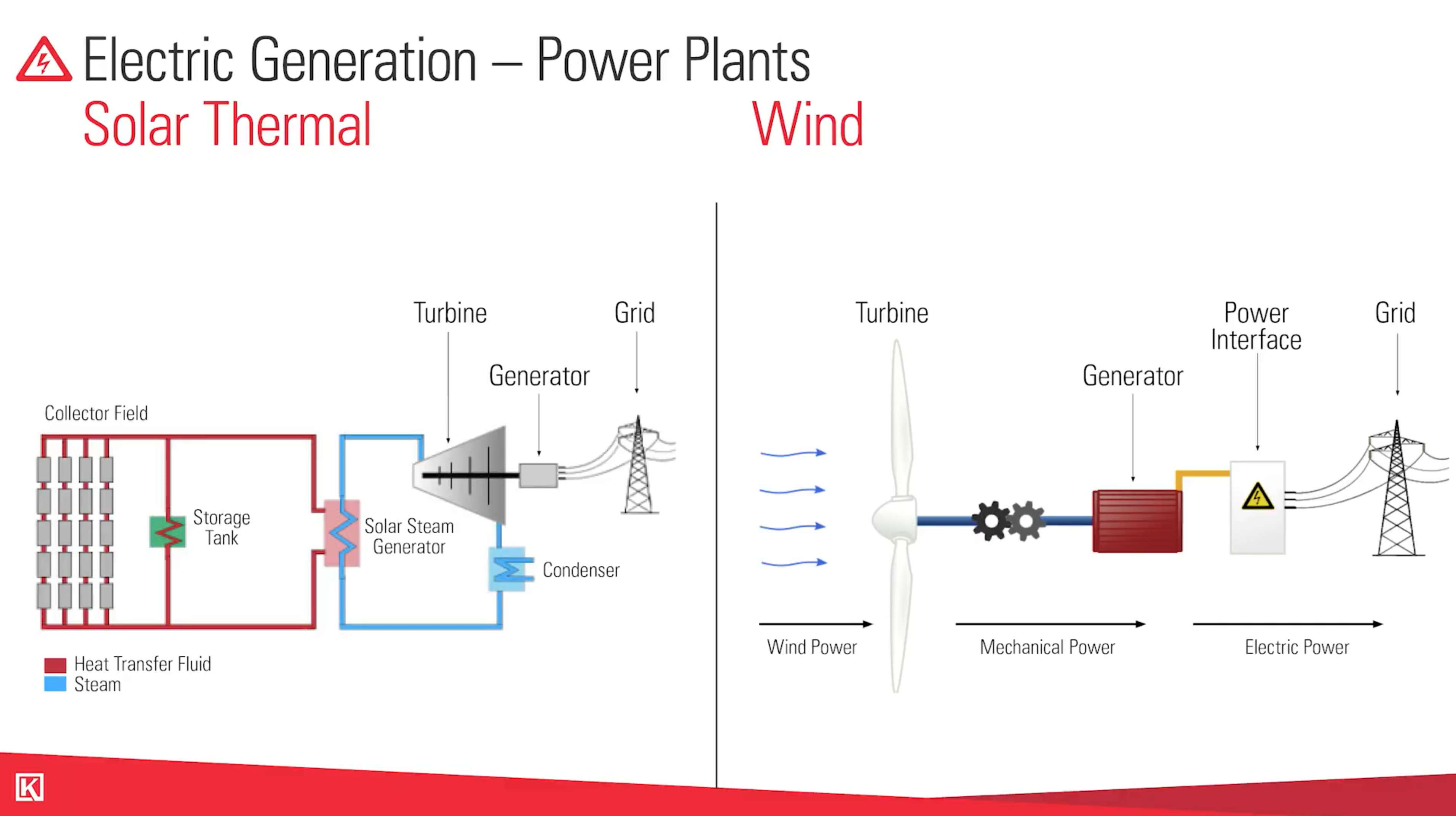
How Does a Wind Power Plant Work?
With wind turbines, large blades spin around with the flow of the wind. From there it goes to a generator, power interface, and out to power lines.
While wind is more energy efficient than solar, they both require unconventional transformers.
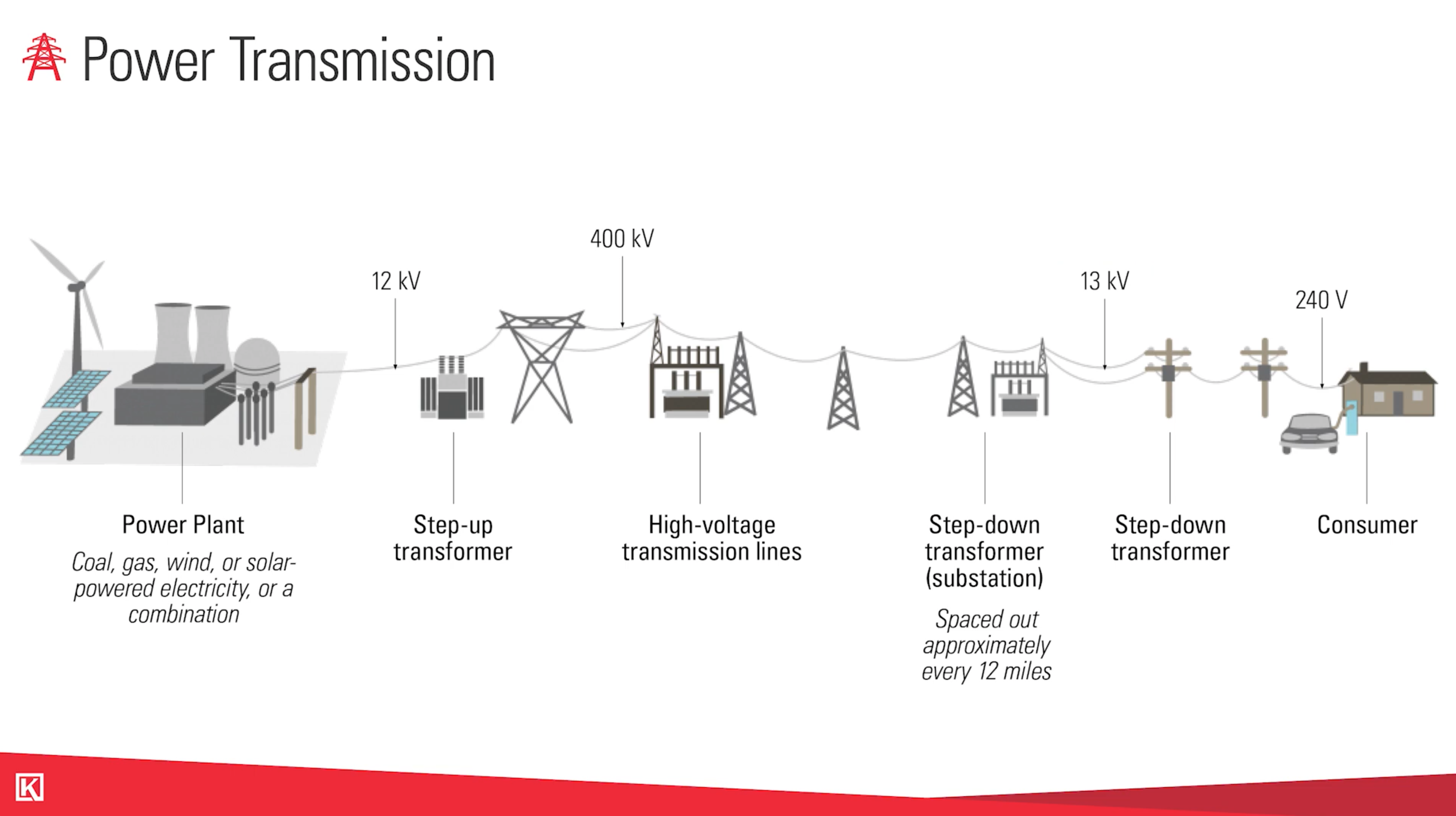
How Does Power Transmission Happen?
After it leaves these different types of plants, the power will follow this typical path:
- Step-up transformer
- High-voltage transmission lines
- Step-down transformer
- Consumer
what are the 3 Main Power Grids in the United States?
- Eastern Interconnection
- Western Interconnection
- Texas Interconnection
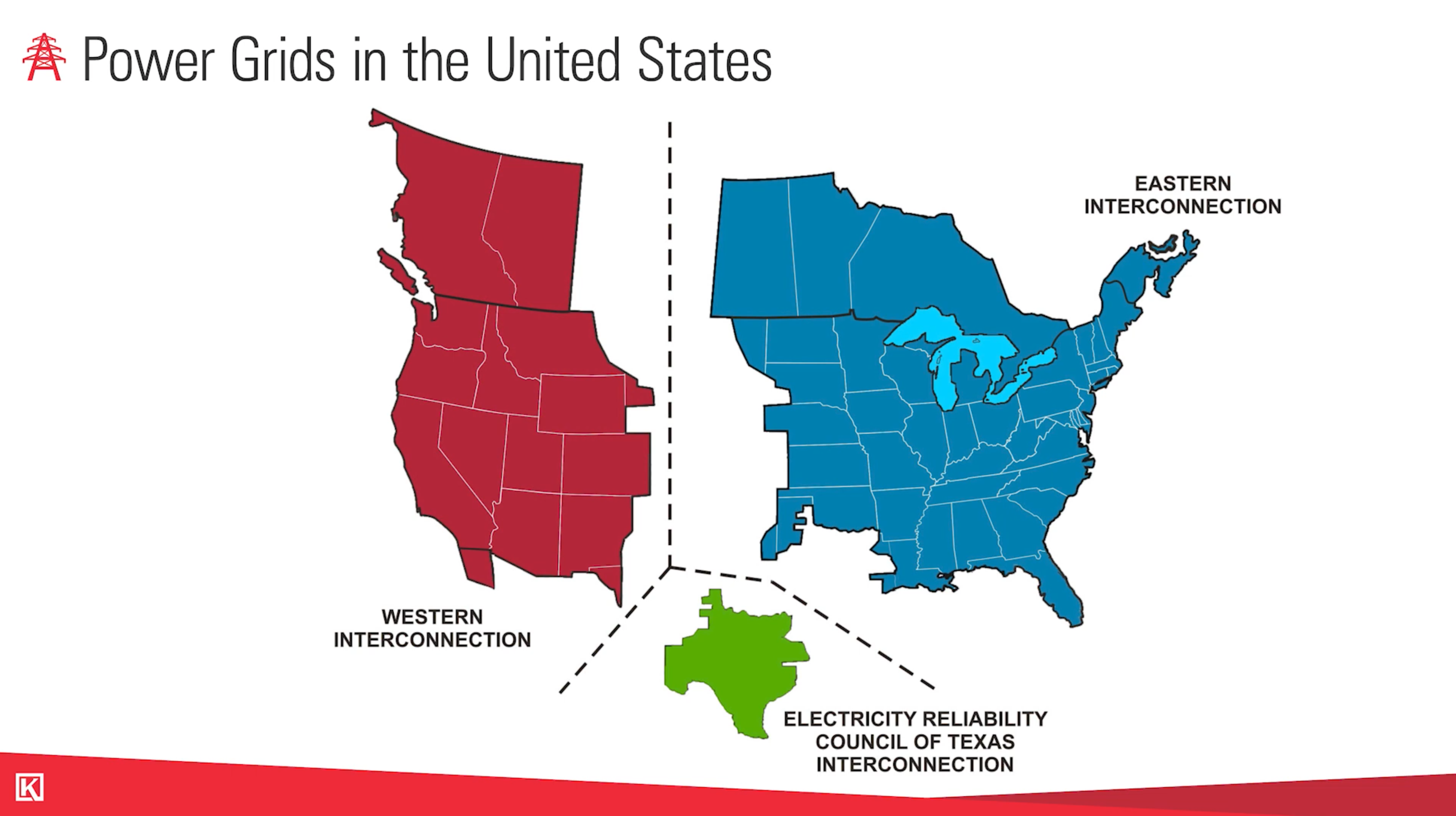
The east and the west coasts of the U.S. are where the industrial revolution kicked off in the 1800s. That's where electricity was needed first, and then over the years the required infrastructure was gradually built up in the middle of the country.
Meanwhile, Texas was having its own industrial boom and wasn't getting the electricity they needed to support it from the coasts. So, they started a local co-op there.
At the beginning of World War II, several of the utilities in Texas agreed to interconnect their systems like the bigger eastern and western interconnections.
Now this co-op—the Electric Reliability Council of Texas, or "ERCOT"—provides 90 percent of the state's load with this co-op of other interconnection companies. The Texas power grid with the electric reliability council of Texas manages approximately 26 million Texas residents.
With these three national power grids, we now have 46,000 miles of transmission lines.
Note that there’s not a whole lot of infrastructure there straight up the Rocky Mountains, where some shale plays are, which is one reason solar panel and battery backup systems are used more in these regions.
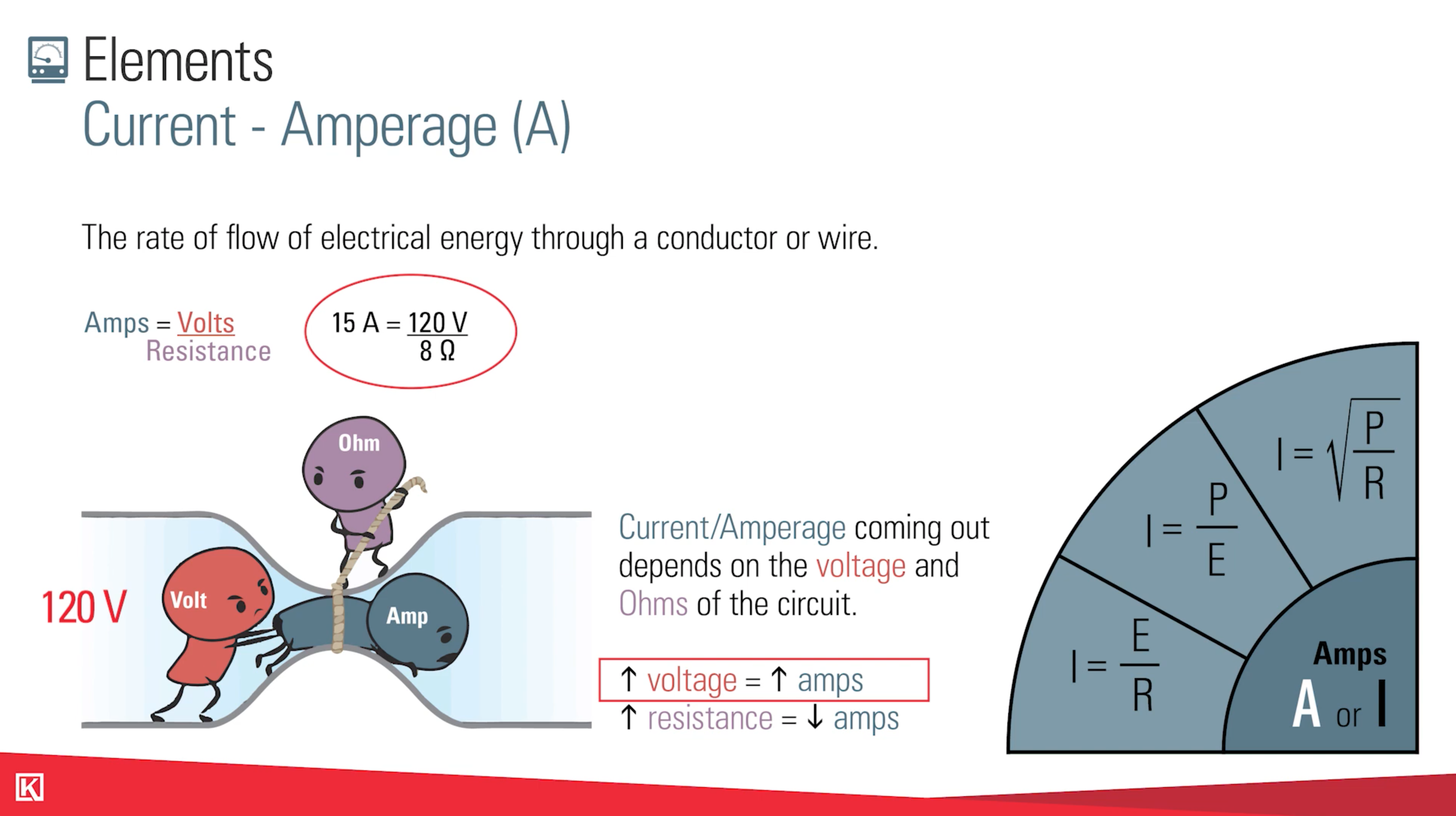
What is Ohm’s Law?
Ohm’s Law is a principle of electricity that allows you to use established formulas to solve for a missing value.
Ohm's Law allows us to convert these 4 electric elements:
- Voltage (Volts)
- Current (Amps)
- Power (Watts)
- Resistance (Ohms)
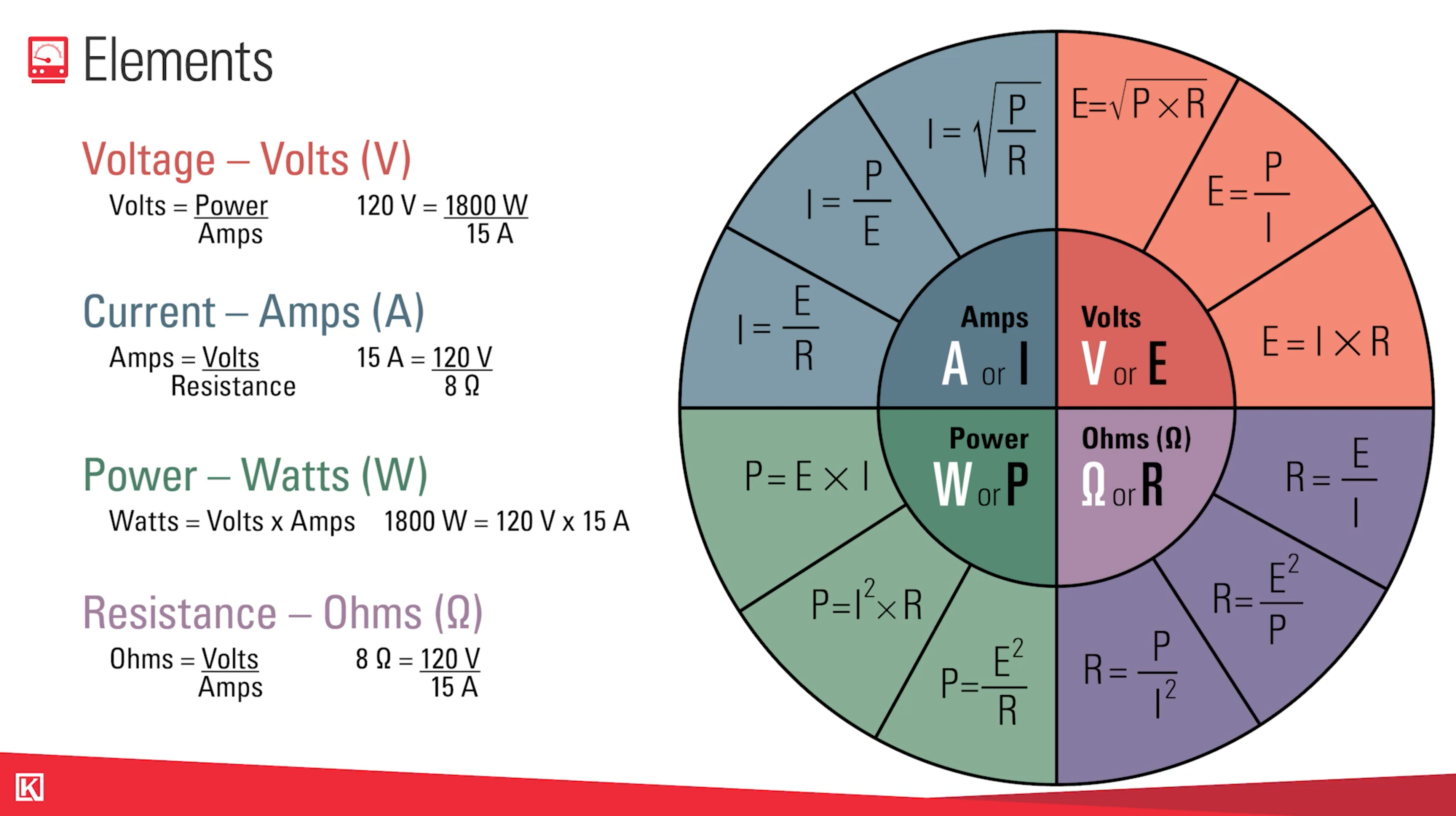
For example, one of the most commonly used terms for power in product literature is Watts. If you need to convert to watts, you can reference your Ohm's Law table and see that if you multiply Volts times Amps, this will give you watts.
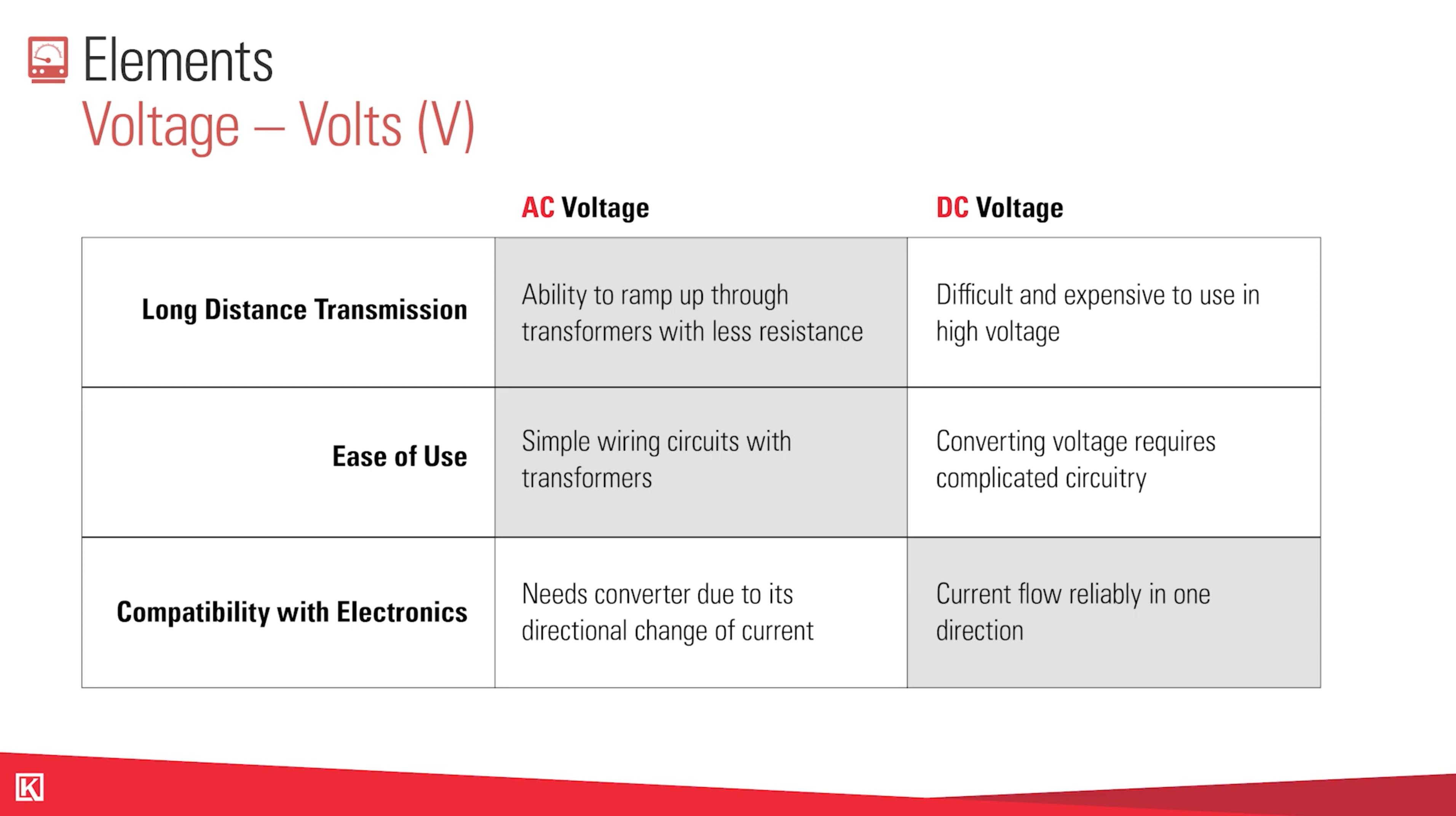
What's the Difference between AC and DC Power?
AC stands for alternating current.
Voltage is defined as the amount of potential energy between two points on a circuit. One point has more charge than the other.
This first picture is a sine wave. It's the AC voltage, it's what you use every day in your house.
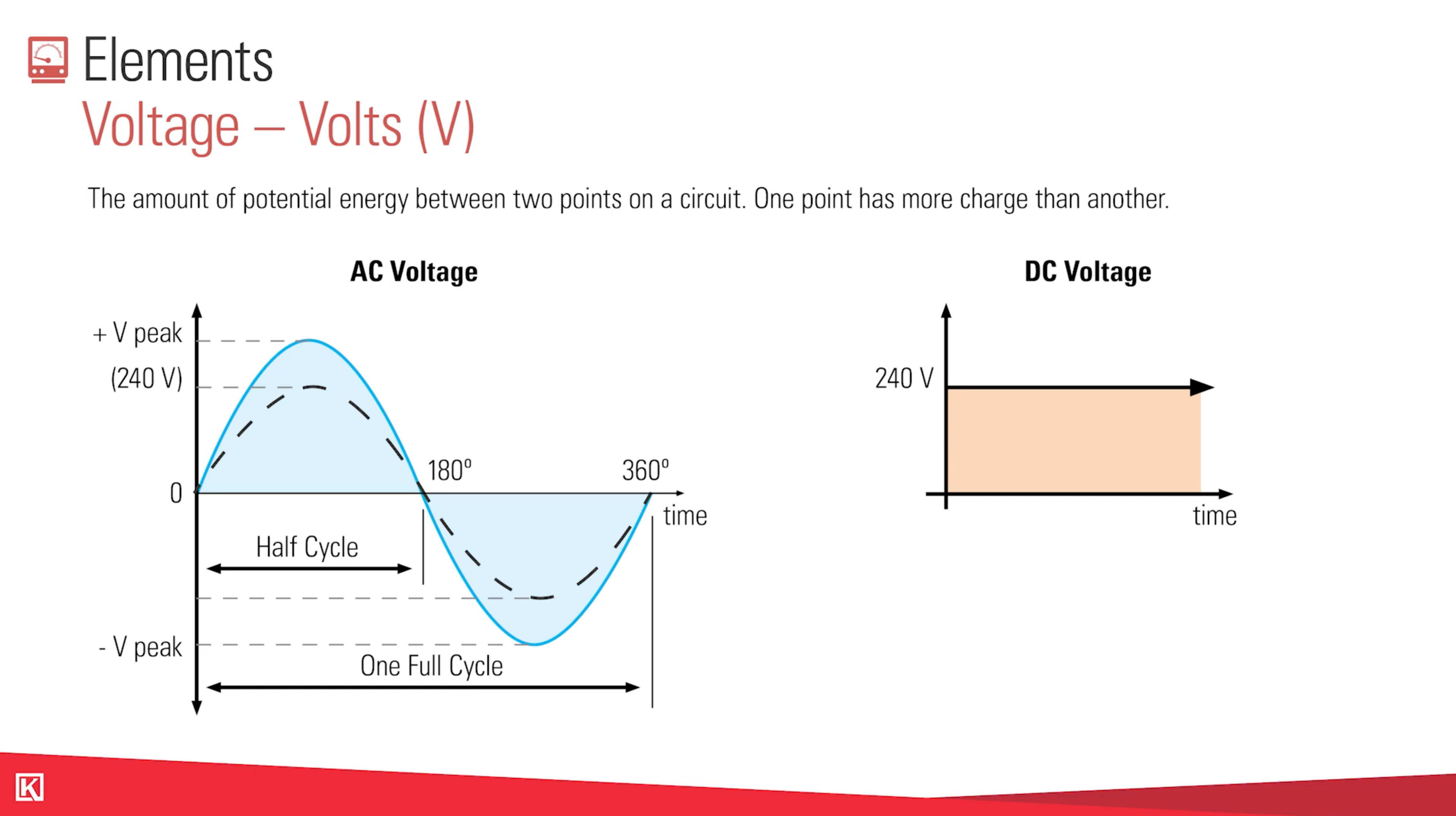
DC, on the other hand, is used in items like car batteries, solar panel packages, or an electronic devices like phone chargers.
DC stands for “direct current.”
DC is a straight, direct current that creates and holds the charge. So while AC is flowing constantly, DC is a bank of power that will run out and need to be recharged.
Are you Ready to harness electricity for your oil & gas operation?
Our line of electric-powered products provide robust, efficient control of your oil and gas processes. To learn more, check out our video 5 Electric Control Products that Reduce Emissions.
To speak with an expert about using electric control products into your operation, contact your local Kimray store or authorized distributor.









































