A Gas Production Unit, or GPU, is actually two pieces of equipment joined together inside one housing: a line heater and a horizontal separator.
In this video, Kyle explains:
- What a gas production unit is
- Where and why gas production units are used
- The phases and sizes of a gas production unit
- The flow path through the unit
Where and Why a Gas Production Unit is Used
To be sellable, gas must be at a certain pressure and it must be dry. Upstream producers use a GPU to accomplish these two things. It reduces the pressure and dries the gas.
The challenge with this process is that when gas pressure is reduced, its temperature drops, which can cause hydrates to form or even freezing to occur. This is where the GPU comes in.
The line heater heats the gas and then the separator dries the gas by knocking out the liquids.
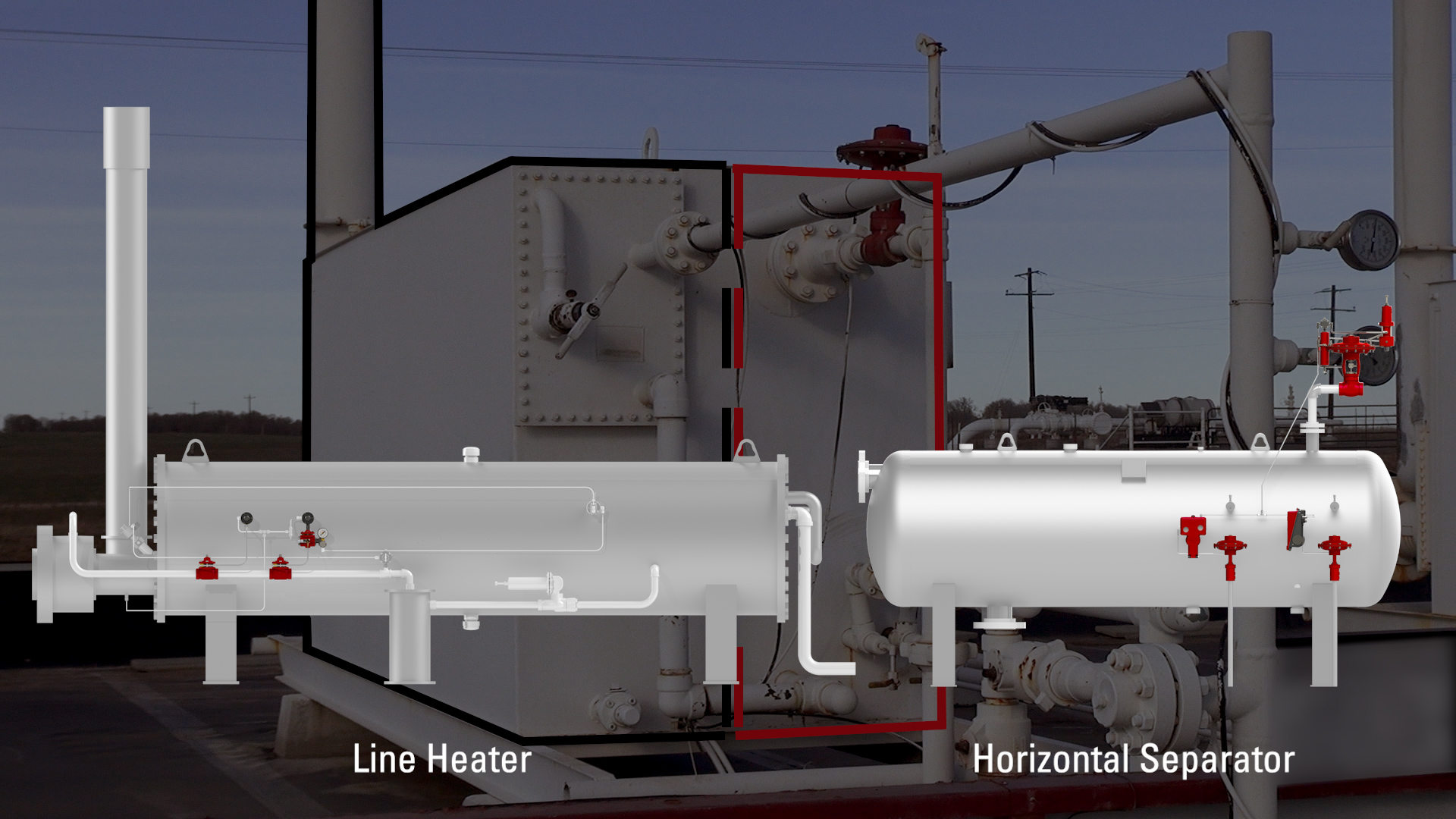
A gas production unit may be a 2- or 3-phase vessel. A 2-phase vessel separates gas and liquids. A 3-phase GPU separates gas, water, and oil. The separation is accomplished in the high-pressure horizontal separator side of the vessel.

The size of the GPU needed will depend on the expected flow rate. This chart below shows common sizes and the gas flow rates that it can handle. This is be useful when sizing Kimray products to be used on this equipment.
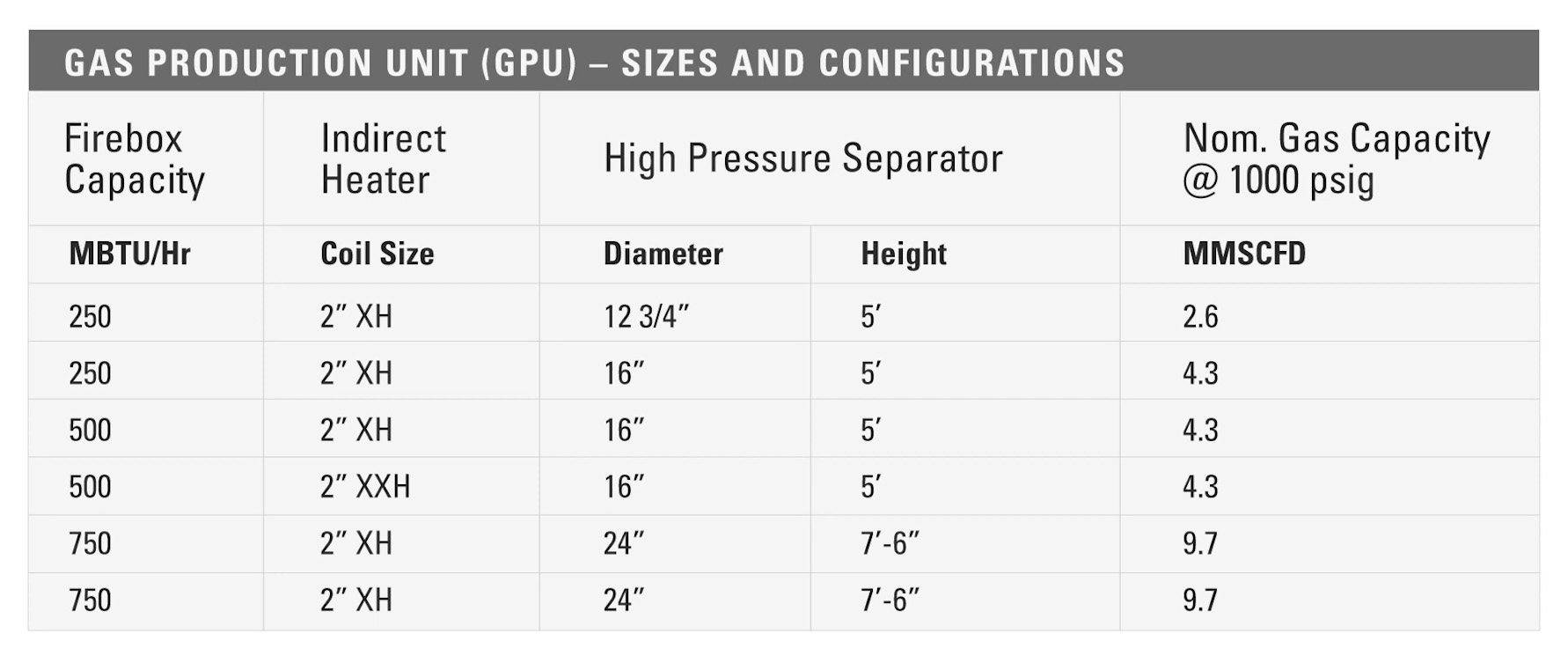
The coil will be rated for 3000 PSI or greater, and the separator will have a working pressure of 1000 PSI or more.
Flow Path through the GPU Line Heater and Separator
The high-pressure well stream coming into the line heater of the GPU is heated to accommodate the large pressure drop that will take place.
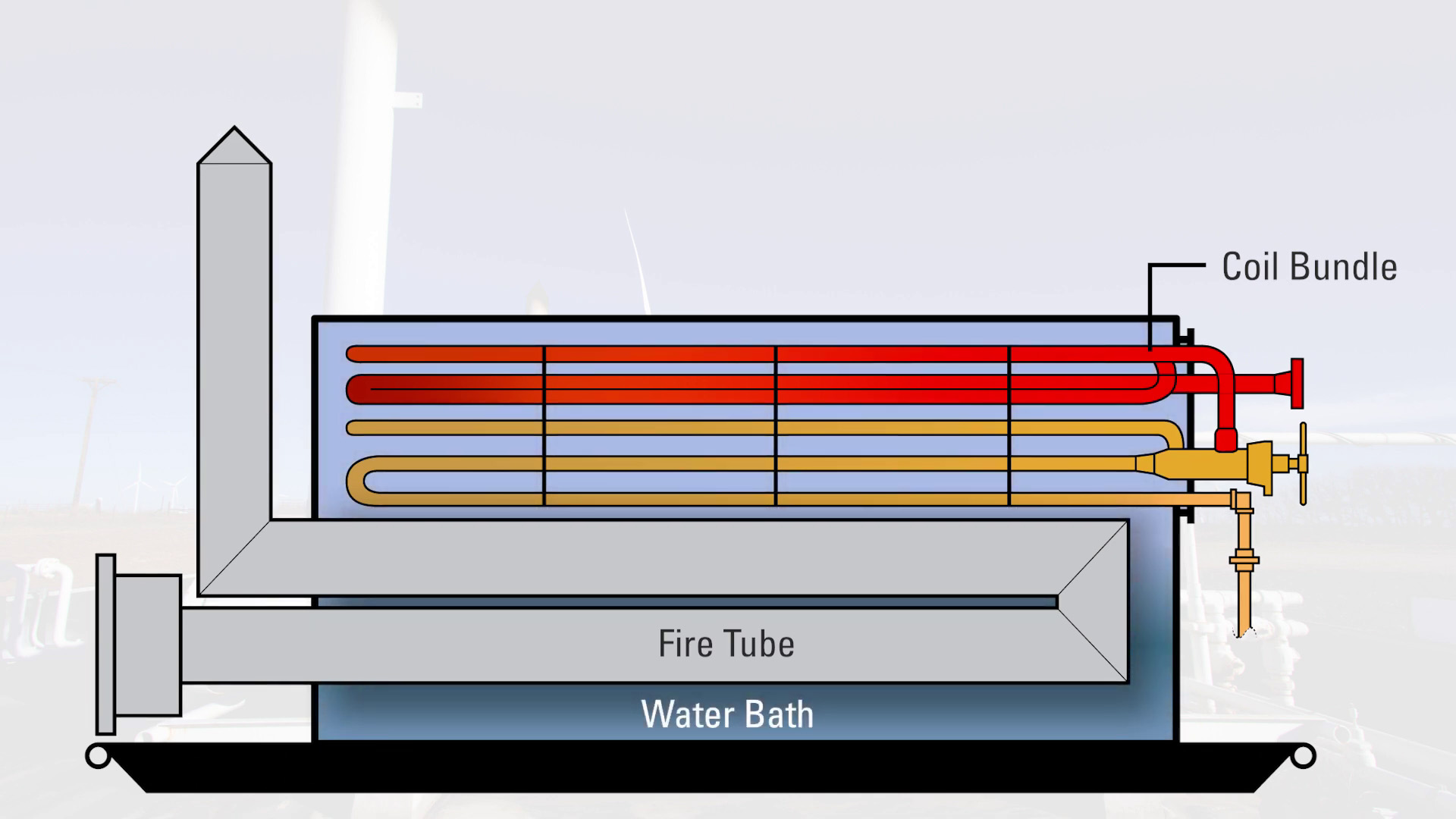
A line heater consists of a firetube and two sets of coils inside a water bath. The firetube, controlled by a burner management system, heats the water bath. The coils containing the well stream then run through the water bath. This heats up the well stream.
After the well stream is pre-heated through the first set of coils, it goes through a choke valve to cut the pressure down to at least the maximum working pressure of the separator. This pressure cut can be as high as 2000 PSI.

With this pressure cut there will be a temperature drop. For every 100 PSI pressure drop there will be a temperature drop of 6-8° F.
After the choke, it goes through the second set of coils, which are also referred to as expansion loop coils. The well stream is then heated again and allowed to expand prior to entering the separator for further processing.
Each of the separated components of the well stream will then go to storage, pipeline, or more separation equipment.
The water will go to disposal or storage, the oil will either go to sales or continue to another vessel for further processing, and if a 3-phase separator is being used, the gas will go to a meter run where it is measured and sold.
To speak with an expert about how to optimize your Gas Production Unit, contact your local Kimray store or authorized distributor.









































